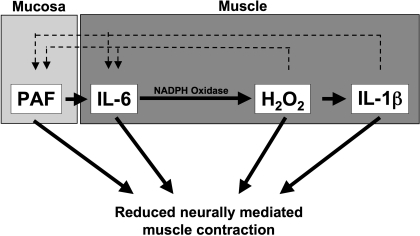
Fig. 2.
Working model for the effect of inflammatory mediators on muscle contraction. Acid reflux in the esophagus causes formation of platelet-activating factor (PAF) by the esophageal mucosa. PAF is then released from the mucosa to activate the circular muscle, causing the sequential production of IL-6, H2O2, and IL-1β. H2O2 and IL-1β induce production of PAF and IL-6, all of which are known to depress neurogenic muscle contraction by inhibiting release of ACh.