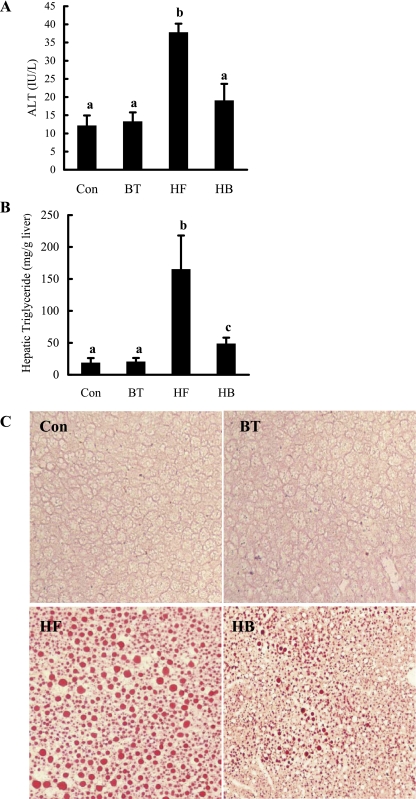
Fig. 2.
Betaine supplementation attenuated liver injury and hepatic fat accumulation in mice fed a high-fat diet. A: plasma alanine aminotransferase (ALT) levels. B: hepatic triglyceride content. C57BL/6 mice were fed a high-fat diet with/without betaine supplementation (1%) in the drinking water for 12 wk. Data are means ± SD (n = 8). Bars with different letters differ significantly (P < 0.05). C: fresh-frozen liver sections were stained with oil red O. Control group animals with/without betaine supplementation had no obvious fat accumulation in the liver. High-fat diet feeding resulted in profound hepatic steatosis, featured by a remarkable amount of fat droplet in the liver. Betaine supplementation significantly decreased hepatic fat accumulation induced by high-fat diet feeding.