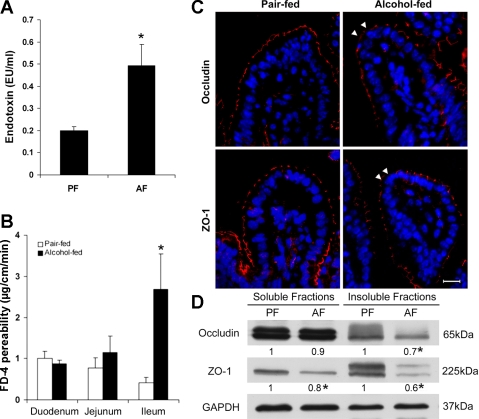
Fig. 2.
Intestinal barrier dysfunction in mice chronically fed alcohol for 4 wk. A: plasma endotoxin. Endotoxin levels were measured by the limulus ameobocyte lystate method. B: intestinal permeability. The penetration of intralumen FITC-dextran (FD-4) to the incubation buffer was determined after incubation of the intestinal sac of duodenum, jejunum, and ileum for 20 min. C: immunofluorescence microscopy of the ileal tight-junction proteins. Arrowheads indicate the disappearance of occludin or zonula occludens (ZO)-1. Scale bar = 30 μM. D: immunoblotting of ileal occludin and ZO-1. The bands were quantified by densitometry analysis, and the ratio to GAPDH was calculated by setting the value of controls as 1. Results are means ± SD (n = 6–8 in A and B, n = 3 in D). *Significantly different (P < 0.05, t-test) from the pair-fed mice.