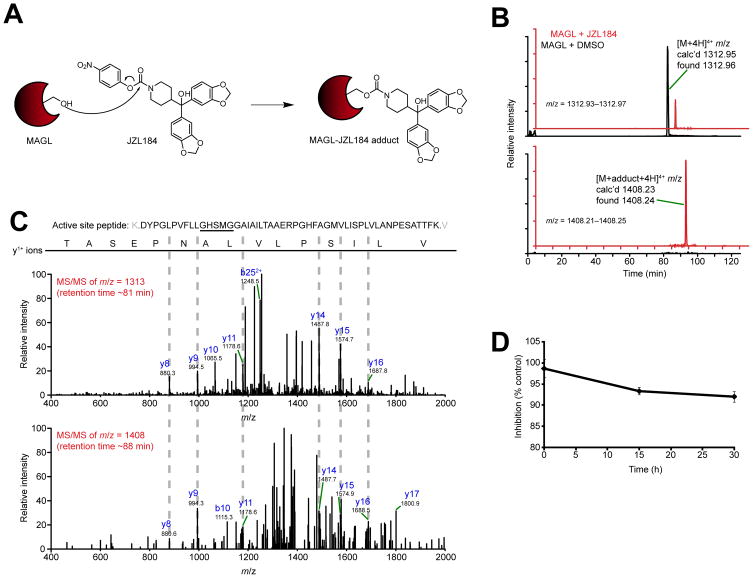
Figure 1.
Mechanism of JZL184 inhibition of MAGL. (A) Proposed mechanism for covalent inactivation of MAGL by JZL184 involving carbamoylation of the enzyme’s catalytic serine nucleophile (Ser122). (B) Extracted ion chromatograms (EIC) of the unmodified (top) and JZL184-modified (bottom) MAGL active site tryptic peptide (amino acids 110–160). Recombinant, purified human MAGL was treated with DMSO (black trace) or JZL184 (200 μM, red trace). The mass window for each EIC, the detected high-resolution mass for each peak, and the charge state for each tryptic peptide are indicated. (C) MS/MS spectra generated by the unmodified and modified active site peptides. Diagnostic y and b ions are identified. All ions are in the 1+ charge state unless otherwise indicated. (D) JZL184-treated MAGL was incubated at room temperature in 50 mM Tris, pH 8.0, and the activity remaining as a percentage of control reactions (treated with DMSO) was measured by 2-AG hydrolysis assays. For (D), data are presented as means ± SEM of three independent experiments.