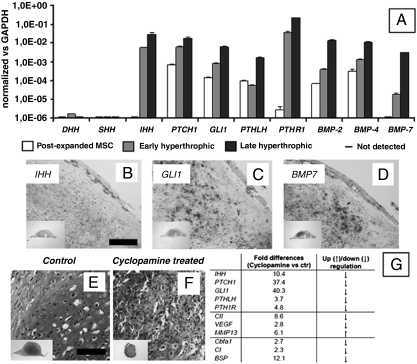
Fig. 4.
Activation of signaling pathways involved in endochondral bone formation in embryos. Signaling pathways typically involved in endochondral ossification were activated in the engineered samples. (A) Real-time RT-PCR analysis indicated that MSC cultured under hypertrophic conditions up-regulated the expression of genes in the IHH signaling pathway (involving IHH, GLI1, and PTCH1), BMPs and parathyroid hormone-related protein signaling (PTHLH, PTHR1). Note that all fold changes in transcript levels are shown in logarithmic scale. (B–D) Four weeks after implantation, the expression of representative genes was assessed by ISH (IHH, GLI1, and BMP7). (E–G) Functional inhibition of the IHH pathway by cyclopamine treatment significantly reduced the expression of genes involved in IHH signaling (IHH, GLI1, PTCH1), PTH signaling (PTHLH, PTHR1), as well as chondrogenic/hypertrophic genes (Col II, VEGF), and osteogenic genes (Cbfa-1, Col I, BSP). Cyclopamine also blocked the differentiation and maturation of the cartilaginous templates in vitro, as assessed by Safranin-O stain. [Scale bar: 200 μm (B–D).] [Scale bar: 400 μm (E and F)].