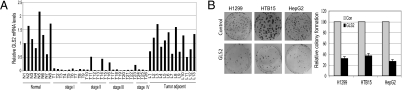
Fig. 7.
Loss of GLS2 expression in hepatocellular carcinomas and the inhibition of colony formation by GLS2 in tumor cells. (A) Loss or significant decrease of mRNA expression of GLS2 in human hepatocellular carcinomas. HCC, hepatocellular carcinoma; N, normal liver. Tumor adjacent tissues: L1–5, tissues with cirrhosis; L6–10, tissues with fatty changes; L11–13, tissues with chronic hepatitis. The GLS2 expression was detected by real-time PCR and normalized with Actin. GLS2 levels of N1 are designated as 1. Samples were provided by Origene Techonologies. P < 0.0001 (normal vs. tumor), P < 0.0001 (tumor adjacent tissues vs. tumor), and P = 0.2367 (normal vs. tumor adjacent tissue). (B) Exogenous GLS2 expression reduces cell colony formation in tumor cells, including H1299, HepG2, and HTB15 cells (P < 0.05).