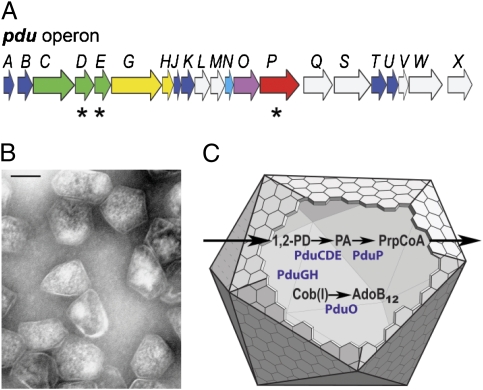
Fig. 1.
Model for the structure and function of the Pdu MCP. (A) Organization of the pdu operon. At least 14 pdu genes (colored) encode proteins that are components of purified Pdu MCPs (27). Asterisks indicate genes that encode polypeptides having potential N-terminal targeting sequences (in the text). Seven genes (blue and cyan) encode shell proteins (27). Homologues of the BMC family of shell proteins are shown in blue. (B) Electron micrograph of purified Pdu MCPs from S. enterica. (Scale bar: 100 nm). (C) Model for B12-dependent 1,2-PD degradation by Salmonella. 1,2-PD is metabolized within the MCP lumen, first to propionaldehyde (PA) and then to propionyl-CoA (PrpCoA). The enzymes that localize to the MCP interior include coenzyme B12-dependent diol dehydratase (PduCDE) and PduP, as well as adenosyltransferase (PduO) and a reactivase (PduGH) that are required for the maintenance of diol dehydratase activity (53–55). The proposed function of the Pdu MCP is to sequester propionaldehyde to minimize its toxicity.