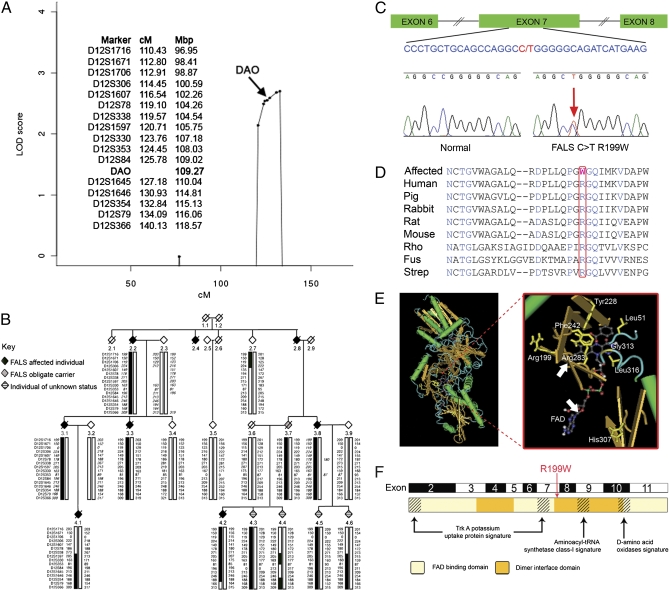
Fig. 1.
Detection of a R199W mutation in DAO and a protein model. (A) Multipoint analysis of family MB1 (Merlin v1.1.2) showing significant maximum parametric LOD scores between markers D12S338 and D12S79. Marker distances (MAP-O-MAT) obtained from http://compgen.rutgers.edu/mapomat/reference.html and sequence map positions obtained from http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov are given for the region containing significant LOD scores on chromosome 12. (B) Haplotype analysis of the 12q21-24 region in family MB1. Allele data for 16 markers in the 12q21-24 region are shown; inferred genotypes are indicated by italics. Markers are listed on the far left hand side of each generation within the family. The haplotype associated with the disease for the index case 4.2 has been indicated by thick solid “boxing.” Cross-over events are indicated by a change in the boxing. Both males and females are indicated by a diamond symbol. A diagonal line indicates that the individual is deceased. (C) Graphical representation of DAO exons 6–8 showing an expansion of part of exon 7. The R199W point mutation is indicated in red together with the corresponding “normal” and “mutated” sequence electrograph. (D) DAO amino acid conservation of the mutated region among eight species. The position of Arg199 (boxed) is indicated in red and variant amino acids in black. Conserved residues are shown in blue. Rho, Rhodotorula gracilis; Fus, Fusarium Solanii; Strep, Streptomyces Avermitilis. (E) Ribbon representation of porcine DAO homodimer (PDB:1AA8, MMDB:5815) and an expanded view of the DAO active site showing the position of Arg199 and FAD (arrows) in relation to key residues including Tyr228, His307, Leu51, Phe242, Arg283, Gly313, and Leu316. (F) DAO protein domains indicating FAD binding and dimer interaction domains together with other potential functional domains.