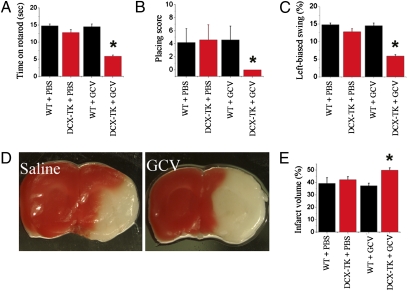
Fig. 2.
Focal cerebral ischemia in Dcx-TK mice. WT (black bars) and Dcx-TK transgenic (DCX-TK, red bars) mice were treated for 14 days with saline vehicle (PBS) or GCV, then underwent MCAO to induce focal cerebral ischemia. Twenty-four hours later, behavioral testing was performed and mice were killed for measurement of infarct size. (A) Rotarod scores, expressed as time (s) mice remained on the rod; lower scores represent more severe deficits. (B) Limb-placing test scores, expressed according to the scale described in Materials and Methods; lower scores represent more severe deficits. (C) Elevated body swing test scores, expressed as percentage turns away from the ischemic hemisphere, as described in Materials and Methods; lower scores represent more severe deficits. (D) Infarct areas (white) in TTC- (red) stained coronal brain sections from PBS- and GCV-treated Dcx-TK mice. (E) Infarct volumes (expressed as percentage hemispheric volume) in PBS- and GCV- treated WT (black) and Dcx-TK (red) mice. *P < 0.05.