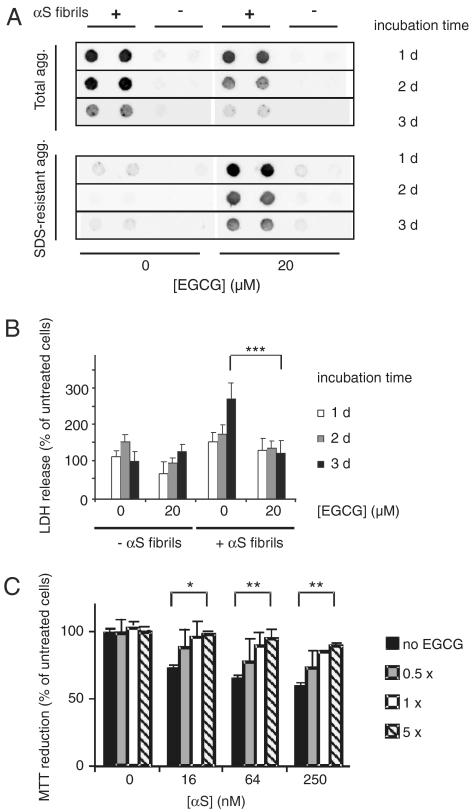
Fig. 3.
EGCG remodels and detoxifies cellular αS aggregates. (A) Fibrillar αS (1 μM) aggregates were introduced into HEK-293 cells expressing wild-type αS (HEK-293 wt αS). After 6 h cells were washed and incubated for 1–3 d in the absence or presence of 20 μM EGCG. NP-40 resistant (total) aggregates as well as SDS-resistant aggregates were quantified by FRA after cell lysis using anti-αS antibody. (B) Cytotoxicity of αS aggregates to HEK-293 wt αS cells was assayed by LDH-release. LDH signals were normalized to cells neither treated with αS aggregates nor treated with EGCG and incubated for 3 d. Values represent means ± SD, n = 8; *** P < 0.0005. (C) Reduction in metabolic activity of PC12 cells after addition of αS fibrils. Fibrils (100 μM) were incubated with different amounts of EGCG for 24 h at 37 °C and diluted into the cell culture media at the indicated concentrations. MTT reduction was normalized to cells neither treated with αS aggregates nor treated with EGCG. Values represent means ± SD (n = 3); * P < 0.01, ** P < 0.001.