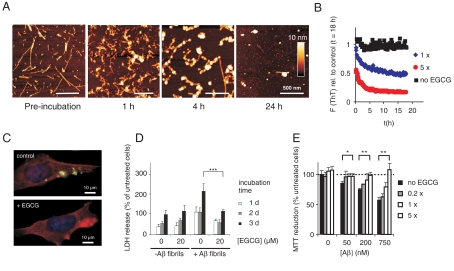
Fig. 4.
EGCG remodels Aβ42 fibrils and oligomers into benign SDS-resistant structures. (A) Fibrillar Aβ42 (15 μM) was incubated with EGCG (15 μM) for up to 24 h in PBS at 37 °C. EGCG-induced remodeling of Aβ42 fibrils into spherical assemblies was monitored by atomic force microscopy. (B) Fibrillar Aβ42 (equivalent 15 μM monomer) was incubated in the absence (Black) or presence of EGCG (15 μM, Blue; 75 μM Red) in PBS at 37 °C. Loss of ThT fluorescence was monitored at time intervals of 10 min, preceded by 5 s shaking each. (C) Immunofluorescence microscopy shows loss of intracellular Aβ aggregates (Green) in 7PA2 cells after ECGG (10 μM) treatment for 3 d. (phalloidin, Red; DAPI, Blue). (D) LDH release in 7PA2 cells after introduction of Aβ42 aggregates. The assay was performed as described in Fig. 3B. Values represent means ± SD, n = 8; *** P < 0.0005. (E) Aβ42 aggregates (15 μM) were incubated with the indicated amounts of EGCG for 24 h at 37 °C. Aggregates were then were diluted into the cell culture media at the indicated concentrations and added to PC12 cells. Metabolic activity was monitored after 3 d by MTT reduction. Values represent means ± SD (n = 3) normalized to cells neither treated with Aβ nor with EGCG; * P < 0.01, ** P < 0.001.