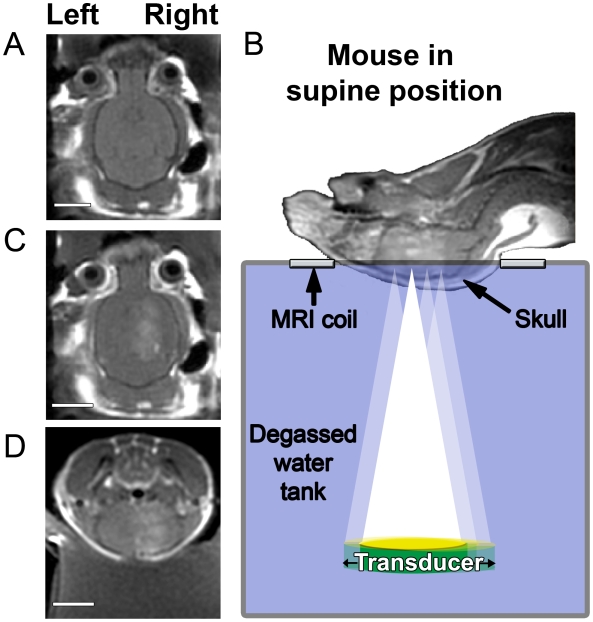
Figure 1. Magnetic resonance imaging-guided focused ultrasound (MRIgFUS) increases the permeability of the blood brain barrier (BBB).
T1-weighted contrast-enhanced MRI scans were used to position ultrasound foci prior to treatment (A) and following transcranial FUS (B–D), were used to monitor the entry of gadolinium in the brain. Mice were positioned in a supine position (B) and injected in the tail vein with microbubbles and gadolinium while ultrasound was applied to 4 aligned spots on the right hemisphere of the brain. Increased BBB permeability was monitored by MRI, visualizing contrast enhancement by the influx of gadolinium (B–D). [A–D: 128×128, TE/TR = 10.4/500.0, FOV = 4cm, Slice 1mm, ETL = 4, 3NEX]. Scale bars: A, C, D = 0.5 cm.