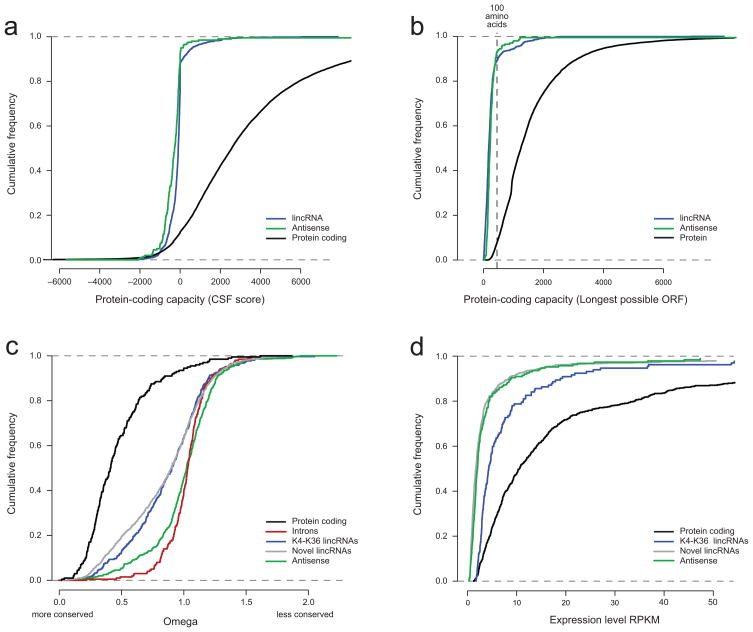
Figure 5. Protein coding capacity, conservation levels and expression of lincRNAs and multi-exonic antisense transcripts.
(a–b) Coding capacity of protein coding, lincRNAs and multi-exonic antisense transcripts. Shown is the cumulative distribution of CSF scores (a) and maximal ORF length (b) for protein coding transcripts (black), lincRNAs (blue) and multi-exonic anti-sense transcripts (green). (c) Conservation levels for exons from protein coding transcripts, lincRNAs, multi-exonic antisense transcripts and introns. Shown is the cumulative distribution of sequence conservation across 29 mammals for exons from protein-coding exons (black), introns (red), exons from previously annotated lincRNA loci (blue), exons from newly annotated lincRNA transcripts (grey), and exons from multi-exonic antisense transcripts (green). (d) Expression levels of protein coding, lincRNAs and multi-exonic antisense transcripts. Shown is the cumulative distribution of expression levels (RPKM) in ESC for protein coding transcripts (black), transcripts from previously annotated lincRNA loci (blue), transcripts from newly annotated lincRNA loci (gray), and multi-exonic antisense transcripts (green).