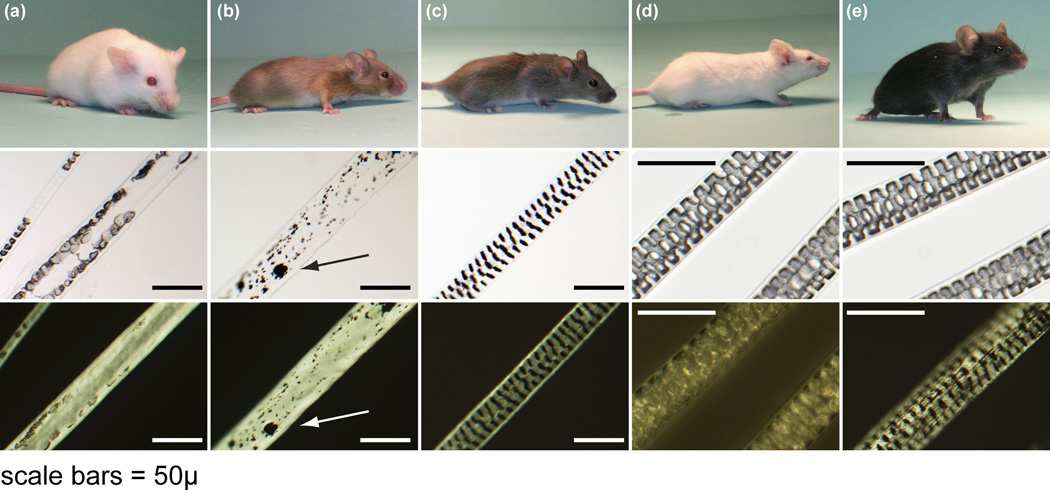
Figure 1.
Hair colour, texture, and fibre quality in a complementation test. (a) AKR/J-hid/hid mice were crossed with (b) SB/LeJ-Foxq1sa/Foxq1sa, Lystbg/Lystbg mutant mice. (c) Their F2 progeny were brown and had normal guard hair fibres with septulate patterns similar to that of (d) normal BALB/cByJ+/+albino and (e) C57BL/6 J+/+black mice. Representative guard hairs are shown below each mouse under white and polarized light to emphasize the defects in the centre of the hair fibres in (a) the hair intereior defect and (b) satin mutant mice. Clumping of melanin pigment (arrow) in (b) the satin mice is because they are also homozygous for the tightly linked beige allelic mutation of the lysosomal trafficking regulator (Lystbg/Lystbg) gene responsible for the beige phenotype (bar = 50 µm).