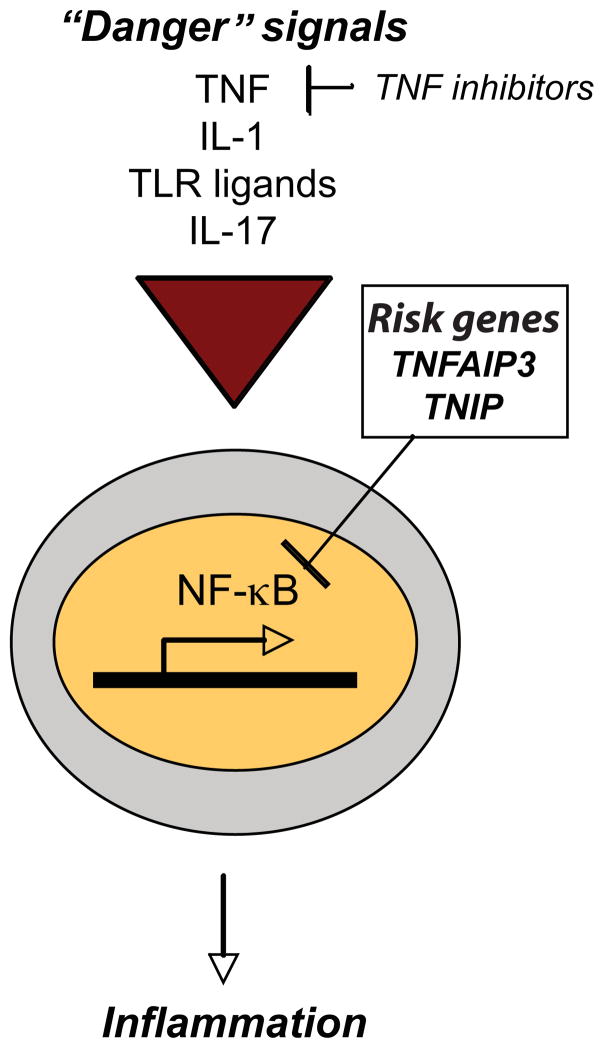
Figure 4. NFκB pathway in psoriasis.
Multiple “danger” signals, including TNF, IL-1, toll-like receptor (TLR) ligands and IL-17, may stimulate the transcription factor, nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells (NFκB), to translocate into the nucleus and promote the transcription of inflammatory genes. Gene polymorphisms that promote unregulated NFkB activity may contribute to psoriasis susceptibility. Genome-wide associated studies (GWAS) have identified polymorphisms in TNFAIP3 and TNIP1, both negative regulators of the NFκB pathway (box).