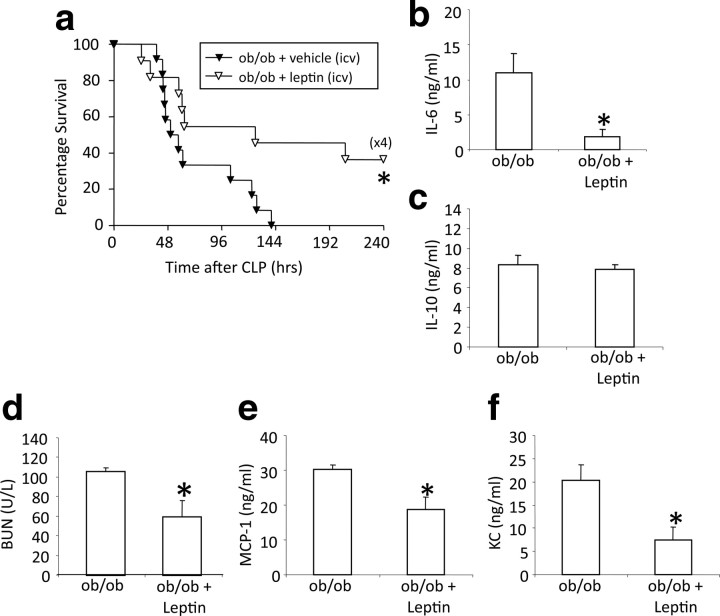
Figure 5.
Leptin treatment in the CNS increased survival and systemic inflammatory response in ob/ob mice. a, ob/ob mice with vehicle (via intracerebroventricular catheter with minipumps, 1 μg/24 h) (n = 13) and ob/ob mice with leptin (intracerebroventricular minipumps) (n = 11) underwent CLP and were monitored for survival for 10 d. Data were pooled from two independent experiments that gave similar results. *p < 0.05 compared with the untreated ob/ob group. b, c, ob/ob mice with leptin treatment in the CNS underwent CLP. IL-6 and IL-10 levels (both nanograms per milliliter) were measured in serum 24 h after CLP. Leptin treatment resulted in a significant decrease of systemic IL-6 levels but no changes of systemic IL-10 levels (n = 4–5 per group). *p < 0.05 compared with the untreated ob/ob group. d, Blood urea nitrogen (BUN) was measured 24 h after CLP in serum. Leptin treatment in the CNS resulted in decreased BUN levels (n = 4–5 per group). *p < 0.05 compared with the untreated ob/ob group. e, f, ob/ob mice with leptin treatment in the CNS underwent CLP. MCP-1 and KC levels (both nanograms per milliliter) were measured in serum 24 h after CLP. Leptin treatment resulted in a significant decrease of systemic MCP-1 and KC levels (n = 4–5 per group). *p < 0.05 compared with the untreated ob/ob group. All values are means ± SEM.