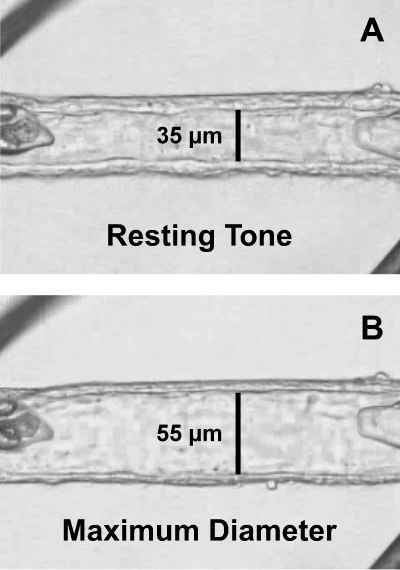
Figure 1.
Image of an isolated human retinal arteriole cannulated with glass micropipettes and secured with ophthalmic sutures. (A) The vessel was transferred to the stage of an inverted microscope and was allowed to develop resting basal tone (35-μm internal diameter) at 55 cm H2O intraluminal pressure. (B) Maximum diameter (55-μm internal diameter) of the vessel was established in Ca2+-free solution containing 0.1 mM sodium nitroprusside. The images were taken through a video port of an inverted microscope.