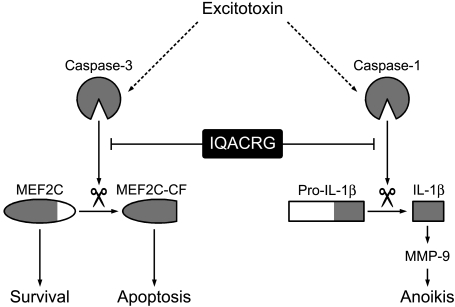
Figure 1.
Schema proposing that prevention of caspase cleavage contributes to the neuroprotective effect of IQACRG. Excitotoxins activate caspases in neurons. For example, activated caspase-3 cleaves MEF2C, resulting in loss of its antiapoptotic transcriptional activity and generation of proapoptotic cleaved fragments (MEF2C-CF). Additionally, caspase-1 cleaves pro-IL-1β to functionally active IL-1β. In turn, IL-1β leads to MMP-9 activation. This pathway is thought to contribute to neuronal cell death by a form of apoptosis known as anoikis. IQACRG binds to caspase substrates, thus protecting them from caspase enzymatic activity. Inhibition of caspase cleavage of substrates, such as MEF2C and pro-IL-1β, contributes to neuronal survival.