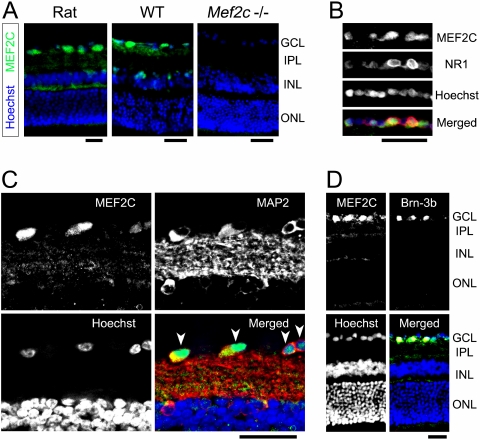
Figure 7.
Localization of retinal MEF2C. Retinal sections were stained immunohistochemically for the transcription factor MEF2C. (A) Immunostaining for MEF2C (green) revealed prominent expression in the GCL of the normal adult rat retina (left). Wild-type mouse retina exhibited similar MEF2C protein localization (center). In contrast, Mef2C conditional knockout mice exhibited no MEF2 immunofluorescence, as expected (right). Cell nuclei were counterstained with Hoechst 33342 (blue). (B) Retinal sections were double-immunolabeled with MEF2C and NMDA receptor subunit 1 (NR1) (green and red, respectively, in merged image). GCL labeling revealed MEF2C protein localization in cells expressing NMDA receptors. (C) Double immunostaining of MEF2C and MAP2 (green and red, respectively, in merged image) clearly displayed individual neurons in the GCL expressing MEF2C (arrowheads). Note that cell nuclei in the GCL show robust MEF2C-immunoreactivity. (D) Double immunostaining for MEF2C and the RGC marker Brn-3b confirmed that MEF2C was expressed in RGCs. Colocalization of MEF2C and Brn-3b (green and red, respectively, in merged image) was evidenced by yellow staining (n ≥ 3 animals for each). Scale bars, 50 μm. IPL, inner plexiform layer; INL, inner nuclear layer; ONL, outer nuclear layer.