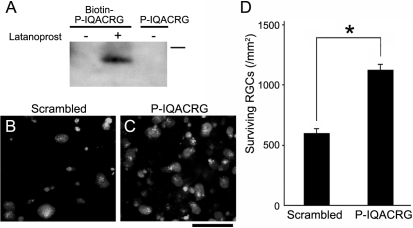
Figure 9.
Subconjunctival treatment with P-IQACRG protects RGCs from NMDA insult. (A) Rats received subconjunctival injection of biotin labeled P-IQACRG (3 nmol) after 12 days of daily instillation of saline or latanoprost. Twenty-four hours after subconjunctival injection of the peptides, retinal lysates were analyzed by avidin-biotin chemistry. Only animals receiving biotin-P-IQACRG plus latanoprost displayed a band representing the biotin-labeled peptide (n = 5 experiments; bar represents 3.5 kDa). (B, C) Rats received daily latanoprost instillation followed by subconjunctival injection of either scrambled peptide or P-IQACRG (30 nmol × 2 days). Before the last subconjunctival administration, NMDA (15 nmol) was delivered intravitreally. Twenty-four hours later, surviving RGCs were assessed by the presence of retrograde label (aminostilbamidine). RGCs were more densely distributed in eyes treated with P-IQACRG. Scale bar, 50 μm. (D) Quantification of surviving RGCs in retinal flat-mounts of animals treated with subconjunctival P-IQACRG or scrambled peptide after NMDA intravitreal injection. Subconjunctival injection of P-IQACRG protected RGCs from NMDA excitotoxicity. Values are mean ± SEM (*P < 0.001 by t-test; n = 9 for each group).