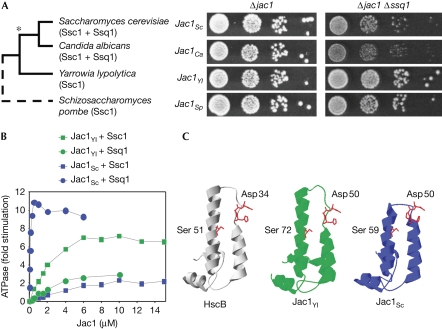
Figure 1.
Altered functional properties and structure of the J-domain distinguishes Jac1 orthologues coexisting with Ssq1. (A) The ability of JAC1 orthologues from several yeast species to support growth when Ssc1 functions in iron–sulphur biogenesis. Left panel: species phylogeny. The asterisk indicates SSC1 duplication. Right panel: Δjac1 and Δjac1 Δssq1 cells harbouring plasmid-borne copies of wild-type JAC1 from the indicated yeast species were plated as 10-fold serial dilutions (starting with approximately 5,000 cells) on rich glucose medium and incubated at 30°C for 3 days. (B) Stimulation of the ATPase activity of Ssc1 and Ssq1 from S. cerevisiae by Jac1Sc and Jac1Yl in the presence of Isu1Sc. ATPase activity in the absence of Jac1 was set to 0. (C) The structure of the J domain of HscB (PDB ID: 1fpo), a Jac1 orthologue from Escherichia coli and structural models of the J domains of Jac1Yl and Jac1Sc. Sc, Saccharomyces cerevisiae; Yl, Yarrowia lipolytica.