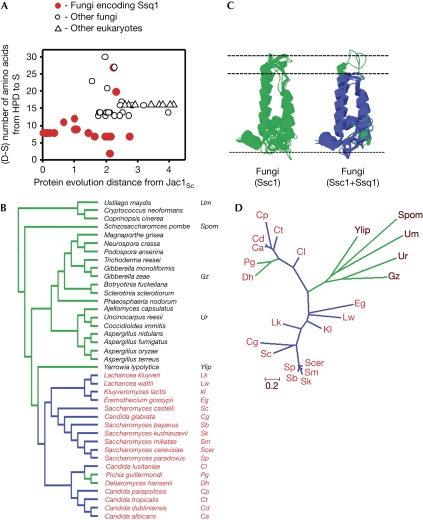
Figure 3.
Across fungal phylogeny, the presence of the ‘short' version of the J domain correlates with the presence of SSQ1. (A) For each Jac1 orthologue, the number of residues between the Asp of HPD and conserved Ser of Helix-III (D–S distance) was plotted against the evolutionary protein distance calculated for each Jac1 orthologue compared with Jac1Sc (supplementary Table S2 online). (B) Fungal phylogeny on the basis of Fitzpatrick et al (2006). Blue branches lead to species encoding a ‘short' J domain; green branches lead to species encoding J domains with a D–S distance greater than 12 amino acids (supplementary Table S2 online). Species encoding Ssq1 are marked in red. (C) The predicted structures of the J domains of Jac1 from the species listed in (B). Blue, ‘short' J domains; green, ‘regular' J domains. (D) Phylogenetic tree inferred from Jac1 structural alignment by maximum likelihood method (details in the supplementary information online). Branches are drawn to scale showing the number of amino-acid substitutions per site.