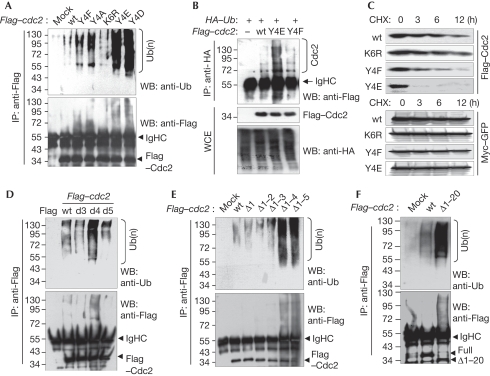
Figure 4.
Phosphorylation or mutation of Cdc2 at Y4 facilitates the polyubiquitination of Cdc2. (A) HEK293 cells were transfected with Flag-tagged wild-type or mt cdc2 plasmids. Cdc2 ubiquitinations were assessed after IP. (B) HEK293 cells were transfected with wild-type or mt Flag–cdc2 plasmids together with HA–Ub plasmid. Cdc2 ubiquitinations were assessed. (C) HEK293 cells, co-transfected with wild-type and mt Flag–cdc2 and Myc–GFP plasmids, were treated with 75 μM CHX for the indicated time periods, and Cdc2 stabilities were assessed. (D–F) HEK293 cells were transfected with wild-type or (D) single amino-acid deletion mt, (E) amino-terminal serial deletion mutants or (F) N-terminal first 20 amino-acid deletion (Δ1–20) mt of Flag–cdc2. Cdc2 ubiquitinations were assessed. The stability of each mt and wild-type Cdc2 was assessed by CHX chase assay (bottom, D,E). All ubiquitination assays were performed after normalization with Cdc2. Cdc2, cell division cycle 2; CHX, cycloheximide; GFP, green fluorescent protein; HA, haemagglutinin; HEK, human embryonic kidney; IP, immunoprecipitation; mt, mutant; PKR, double-stranded RNA-activated protein kinase; Ub, ubiquitin; WB, western blot; wt, wild type.