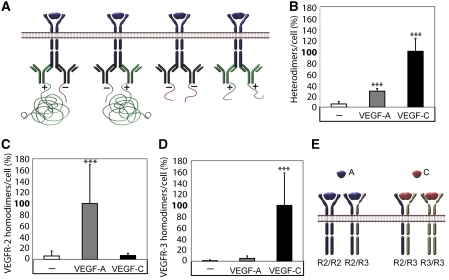
Figure 3.
VEGFR2/-3 homo- and heterodimers induced by VEGFA or VEGFC. (A) Schematic outline of primary antibody ligation with oligonucleotide plus and minus strands to detect VEGFR homodimers. Only pairing of antibodies with plus and minus strands allow initiation of the rolling-circle amplification. (B) VEGFR2/-3 heterodimerization. HSaVECs were treated for 8 min with either VEGFA or VEGFC. Heterodimerization was 3–4-fold more efficiently induced by VEGFC. n=6. (C) VEGFR2 homodimers. Equal mixtures of VEGFR2 monoclonal antibodies ligated with plus and minus strands of oligonucleotides (as outlined in A) were used to detect VEGFR2 homodimers on HSaVECs treated for 8 min with VEGFA or VEGFC as above. n=6. (D) VEGFR3 homodimers. Equal mixtures of VEGFR3 monoclonal antibodies ligated with plus and minus strands of oligonucleotides were used to detect VEGFR3 homodimers on HSaVECs treated for 8 min with VEGFA or VEGFC. n=6. (E) Schematic outline of VEGFR homo- and heterodimerization induced by VEGFA or VEGFC. Note that the relative distribution of homodimers versus heterodimers cannot be accurately determined due to the inherent difference in affinity of different antibodies. Asterisks in panels B–D indicate the degree of significance (***P<0.001).