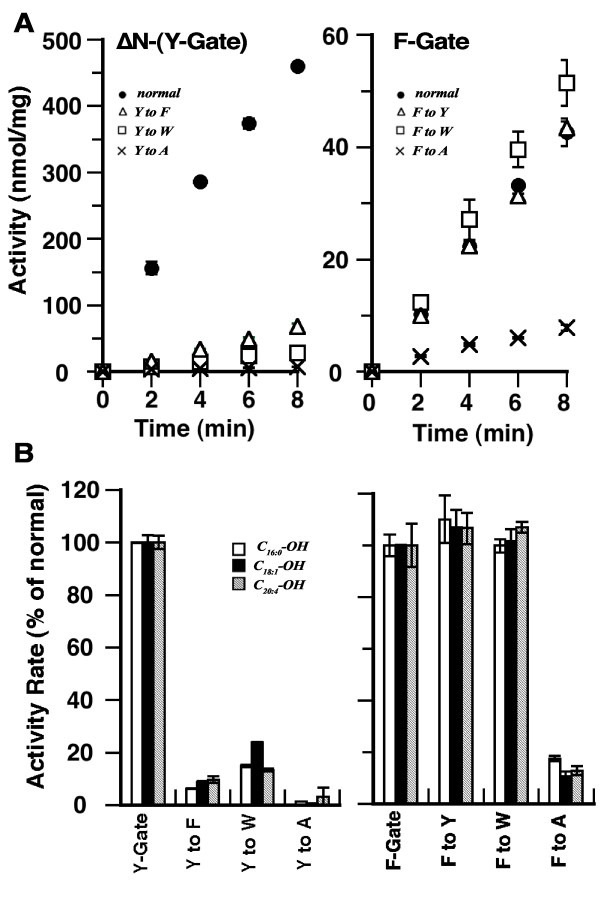
Figure 3.
Role of the aromatic residue at position 319. The tyrosine residue of isoform 1 (Y-Gate) was changed by site-directed mutagenesis to a phenylalanine (Y to F), a tryptophan (Y to W) and an alanine (Y to A). The phenylalanine residue of isoform 2 (F-Gate) was changed to a tyrosine (F to Y), a tryptophan (F to W) and an alanine (F to A). Because activity of isoform 1 was low, its amino-terminus was removed to increase activity of the mutant forms. Data obtained with ΔN-Y-Gate construct and full-length F-Gate isoform are presented. Measurements were also performed with the full-length Y-Gate version and confirmed findings obtained with the ΔN version. Average and the standard deviation of 3 different experiments are shown. A. Activity obtained with the ΔN-Y-Gate mutants set (left) and with the F-Gate mutants set (right) in presence of 5 μM (14C)-C16:0-OH. Left panel: normal Y-Gate (filled circles); Y319 to W319 (triangles); Y319 to F319 (squares); Y319 to A319 (crosses). Right panel: normal F-Gate (filled circles); F319 to W319 (triangles); F319 to Y319 (squares); F319 to A319 (crosses). B. Activity measurements were performed with 5 μM (14C)-C16:0-OH (open bar), (14C)-C18:1-OH (filled bar) or (14C)-C20:4-OH (hatched bar). Activity rates were calculated from 0 to 8 minutes (as shown in panel A). The values obtained for the normal forms were arbitrary set at 100%, and the activity rates of the corresponding mutated Y or F-Gate form, as indicated, were calculated relative to them.