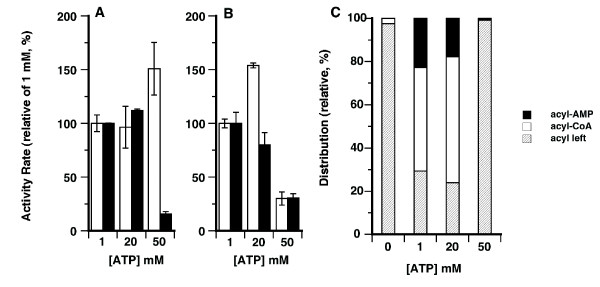
Figure 5.
ATP requirement and detection of acyl-AMP intermediate species. A and B. Activity measurements were performed as described in the legend of Figure 2 with the full-length isoforms (open bar) and the respective ΔN-truncated versions (filled bar) of isoform 1 (Y-Gate) (panel A) and of isoform 2 (F-Gate) (panel B). Assays were performed in presence of 10 μM (14C)-C18:1-OH and ATP concentrations were 1, 20 and 50 mM, as indicated. Relative activity rate values are presented in percent of the rate values obtained in presence of 1 mM of ATP. The actual differences in activity of these enzymes are shown in Figure 2. For each ATP concentration value, the average and the standard deviation of 3 to 5 different experiments is shown. C. Distribution of (14C)-C18:1-OH (acyl leftover), (14C)-C18:1-AMP (acyl-AMP) and of (14C)-C18:1-CoA (acyl-CoA) present in reactions performed without (0), or with addition of 1, 20 and 50 mM ATP, as indicated. Reactions were performed with 10 μM (14C)-C18:1-OH and 1 μg of isoform 2 for 10 minutes at 30°C. Compounds were spotted on silica plates and separated by thin-layer chromatography. For each radiolabeled compound, the intensity of the spot was quantified, and its contribution to the total radiolabeled intensity under each condition was calculated as follows: (14C-species/sum of all 14C -species)*100. Note that at 50 mM ATP, the amount of unreacted (14C)-C18:1-OH (acyl leftover) was as high as under condition without addition of ATP (0 mM).