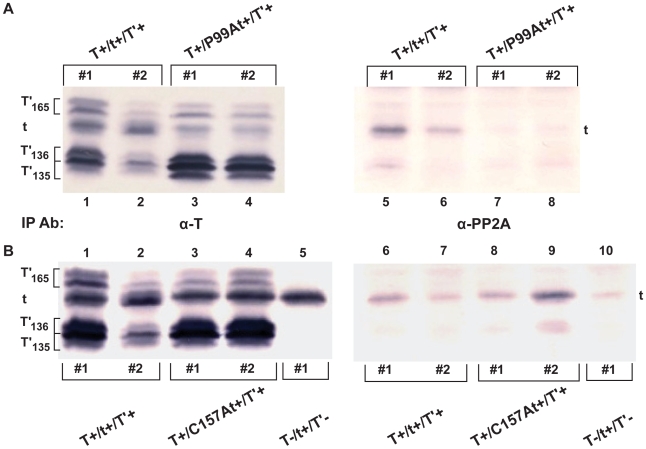
Figure 3. Interaction of mutant JCV tAgs with PP2A.
Interactions between PP2A and wild-type tAg and (A) tAg-mutant P99A or (B) C157A were compared. 3T3 cells were stably transfected with DNA constructs expressing JCV early proteins under the control of SV40 promoter-enhancer signals. Lysates of these cells were subjected to IP with the anti-T monoclonal antibody PAb 962 (α-T) or anti-PP2A antibody (α-PP2A). The amount of total cell protein subjected to IP with anti-PP2A antibody (lanes 5–8, Panel A; lanes 6–10, Panel B) was five times that used with the anti-T antibody (lanes 1–4, Panel A; lanes 1–5, Panel B). Samples were electrophoresed on 18% SDS-polyacrylamide gels and transferred to nitrocellulose membranes. WB was performed using a cocktail of anti-T monoclonal antibodies. Results for two independently-derived cells lines (#1, #2) containing DNA constructs that either encode all 5 JCV wild type early proteins (T+/t+/T′+; Panel A, lanes 1,2,5,6, Panel B, lanes 1,2,6,7) or wild type TAg, T′165, T′136 and T′135 plus tAg mutant P99A (T+/P99At+/T′+; Panel A, lanes 3,4,7,8) or C157A (T+/C157At+/T′+; Panel B, lanes 3,4,8,9) are shown. A single 3T3 cell line expressing tAg only (T−/t+/T′−) was isolated and tested for PP2A binding (Panel B, lanes 5, 10). Panels A and B of this figure each represent proteins electrophoresed on a single gel and transferred to a membrane, which was then cut in half and each half developed for different lengths of time.