Figure 4.
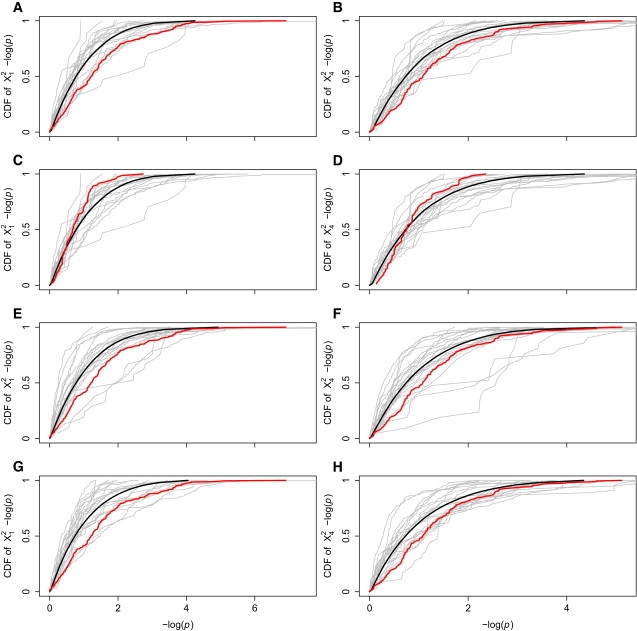
Comparative Gene Pair CDFs
These plots show the cumulative distribution functions (CDFs) of permutation – log(p) computed between the gene pair of interest in red, 20 comparison gene pairs in gray, and the average CDF of all comparison gene pairs in black. In the top row, – log(p) between ZP3R and ZP3 (red) is compared to – log(p) between random gene pairs on chromosomes 1 and 7 (gray) and the average comparative gene pair – log(p) distribution (black) for (A) X12-based and (B) X42-based permutation p values. In the second row, – log(p) between PIP5K1A and DPY19L1 (red) is compared to – log(p) between random gene pairs on chromosomes 1 and 7 (gray) and the average comparative gene pair – log(p) distribution (black) for (C) X12-based and (D) X42-based permutation p values. In the third row, – log(p) in ZP3R-ZP3 (red) are compared to – log(p) between ZP3R and 20 genes on chromosome 7 (gray) and the average – log(p) distribution between ZP3R and chromosome 7 genes (black) for (E) X12-based and (F) X42-based permutation p values. In the bottom row, – log(p) in ZP3R-ZP3 (red) is compared to – log(p) between ZP3 and 20 genes on chromosome 1 (gray) and the average – log(p) distribution between ZP3R and chromosome 7 genes (black) for (G) X12-based and (H) X42-based permutation p values.
