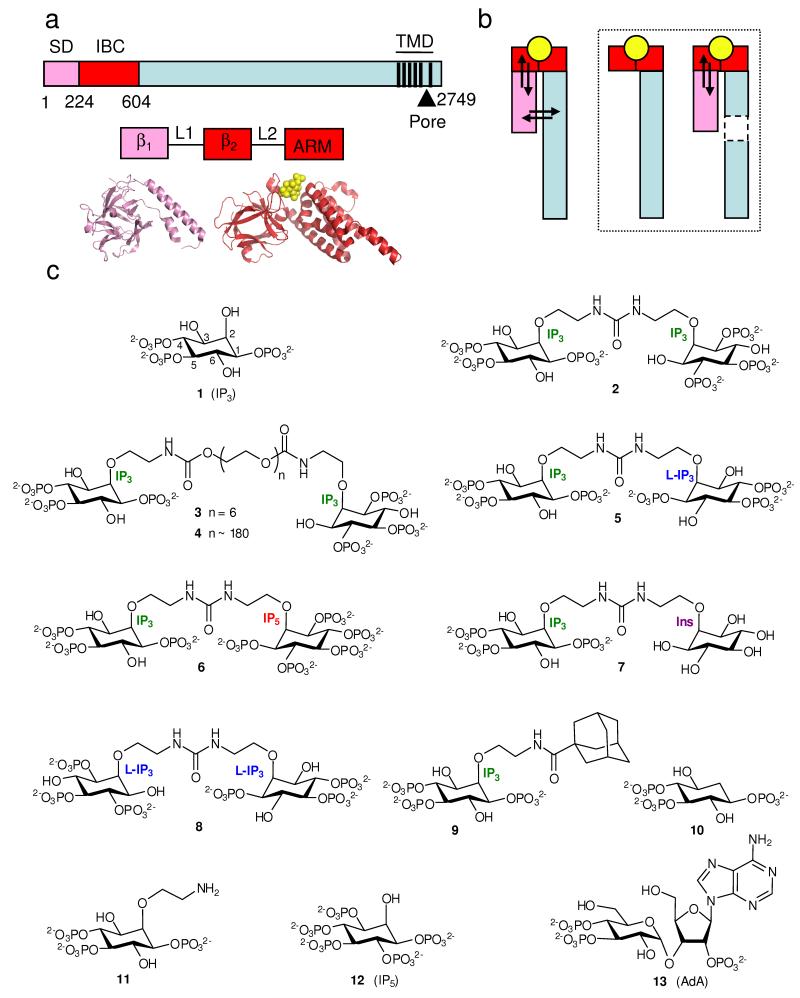
Figure 1.
Structure of the IP3R and its ligands. (a) Key domains of IP3R (numbering from rat IP3R1, accession code NM_001007235). Pink denotes the SD (residues 1-223), red the IBC (224-604), and black vertical lines represent TMD. The SD (β1) and IBC (β2 and armadillo-like repeat, ARM) comprise 3 stably folded domains connected by flexible linkers (L1 and L2)34. Crystal structures are shown below3,33. (b) Agonist binding (yellow) to a discrete site on the receptor (IBC for IP3R, red) evokes conformational changes that propagate through the receptor and which then affect (arrows) the binding site. Removal (boxed diagrams) of a domain through which conformational changes must pass prevents this energetic interplay between conformational changes and binding. (c) Structures of the ligands used.