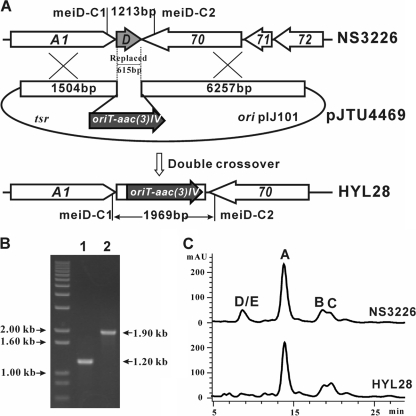
FIG. 5.
Gene replacement of meiD. (A) Schematic representation of the replacement of a 615-bp internal fragment of meiD by the 1.40-kb oriT-acc(3)IV cassette. Wild-type NS3226 should yield a 1.20-kb PCR-amplified product, and mutant HYL28 should yield a 1.90-kb product by using primers meiD-C1 and meiD-C2. (B) Confirmation of the meiD-deleted mutant via PCR amplification. (C) HPLC analysis of wild-type NS3226 and meiD mutant HYL28. The peaks of meilingmycins D and E disappeared in mutant HYL28, and meilingmycins A, B, and C are still produced by the mutant.