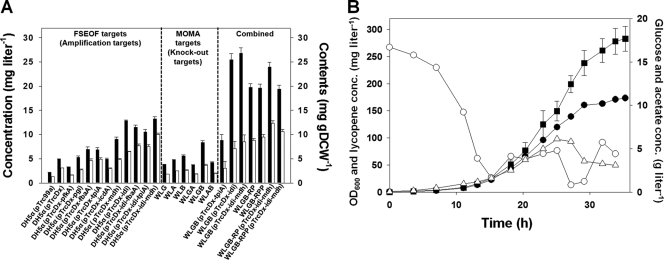
FIG. 3.
Identification of gene targets for enhanced lycopene production by FSEOF, MOMA, and their combination. (A) Production of lycopene by recombinant E. coli strains engineered based on the results of FSEOF, MOMA, and their combination. All strains harbor the plasmid pLyc184 in addition to the plasmid shown. The lycopene concentrations (mg liter−1) and contents (mg g DCW−1) are shown by black and white bars, respectively. Error bars show standard deviations. Strains and plasmids used are described in Tables 1 and 2. All experiments were carried out in triplicate. The products of genes shown in the plasmid names are phosphofructokinase (pfkA), phosphoglucose isomerase (pgi), fructose-bisphosphate aldolase (fbaA), triosephosphate isomerase (tpiA), isocitrate dehydrogenase (icdA), malate dehydrogenase (mdh), and isopentenyl diphosphate isomerase (idi). (B) Lycopene production by batch-fed cultivation of WLGB-RPP(pTrcDx-idi-mdh, pLyc184). Closed circles, optical density at 600 nm (OD600); open circles, glucose concentration (conc.); open triangles, acetic acid concentration; closed squares, lycopene concentration. Error bars represent standard deviations.