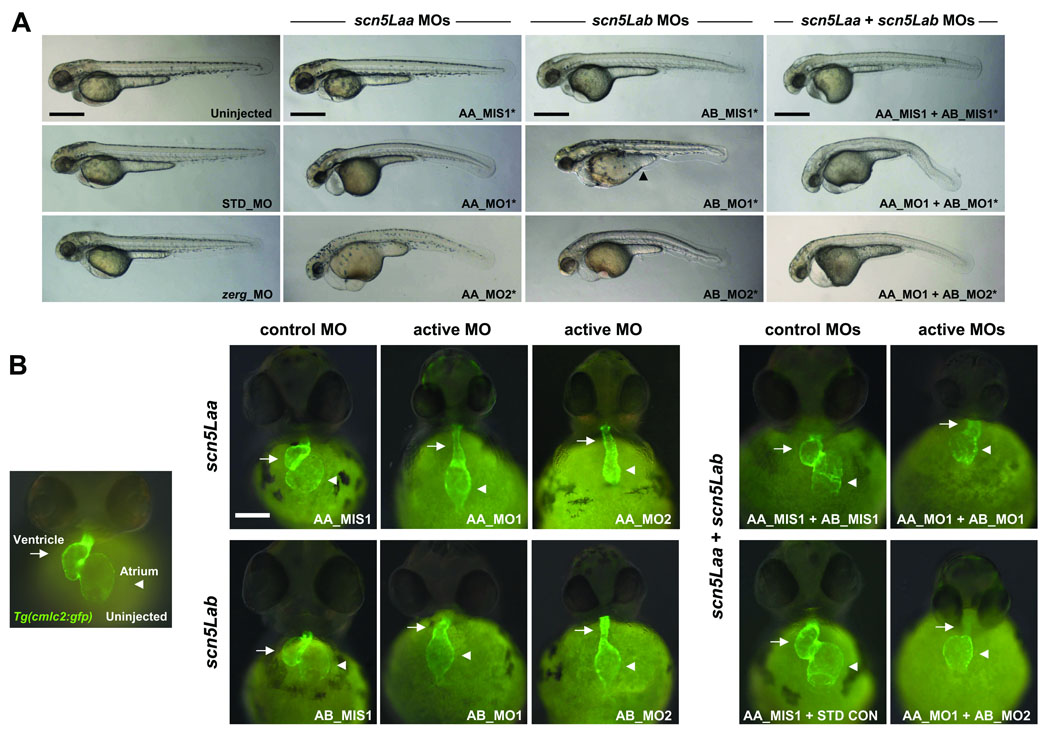
FIGURE 2. Zebrafish scn5Laa and scn5Lab are each required for normal cardiac development.
A. Embryos at 58–62hpf following treatment with active or control antisense morpholinos. All embryos were also treated with the p53 morpholino. Injection of p53 morpholino alone did not cause any identifiable phenotype (Online Figure VII). Note that head size is reduced in all sodium channel morphants and that many embryos injected with AB_MO1 display a yoke sac extension abnormality (arrowhead). All scale bars = 500µM. B. Cardiac developmental defects in morphant Tg(cmlc2:GFP) embryos. AA_MO1 and AB_MO2 caused the most severe cardiac phenotypes at the lowest doses. Knockdown of both scn5Laa and scn5Lab resulted in cardiac defects that were more severe than knockdown of either sodium channel alone, particularly with respect to ventricular morphogenesis. Arrows = ventricle. Arrowheads = atrium. Scale bar = 150µM. Treatments are as labeled: STD_MO = standard control morpholino, zerg_MO = cardiac potassium channel morpholino, AA_MIS1 = scn5Laa 5-mismatch control morpholino, AA_MO1 = scn5Laa translation-blocking morpholino (ATG initiation site), AA_MO2 = second scn5Laa translation-blocking morpholino (5’UTR), AB_MIS1 = scn5Lab 5-mismatch control morpholino, AB_MO1 = scn5Lab splice-blocking morpholino (E6I6), AB_MO2 = second scn5Lab splice-blocking morpholino (E25I25).