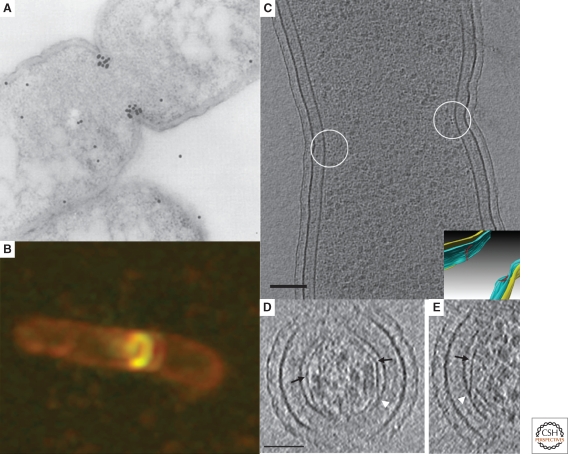
Figure 1.
Microscopy of FtsZ. (A) Immunolocalization of FtsZ in a dividing Escherichia coli cell. The location of FtsZ is indicated by the black dots, which are gold-labeled antibodies. Adapted from (Lutkenhaus 1993) with permission from Blackwell Publishing ltd. (B) Fluorescent light microscopy image of E. coli cells expressing low levels of FtsZ-GFP showing the formation of a new FtsZ ring (gold) in a dividing cell (outlined in red). Reprinted from (Margolin 1998), © 1998, with permission from Elsevier Ltd. (C) An 8-nm thick cryo-tomographic slice through a dividing Caulobacter crescentus cell showing FtsZ filaments in cross-section (small dark dots near the center of the circles next to the membrane). Scale bar 100 nm. The inset shows the 3-D segmentation of the same cell. The inner membrane, outer membrane and the FtsZ arclike filaments are colored in blue, yellow and red, respectively. (D) and (E) 6.7-nm thick tomographic slices containing examples of straight and curved (white arrow) segments of FtsZ filaments. Abrupt “kinks” were sometimes seen (black arrows) as well as direct connections of straight filaments to the membrane (white arrowheads). Scale bar 50 nm. Fig. 1C–E adapted from (Li et al. 2007) with permission from Nature Publishing Group.