Abstract
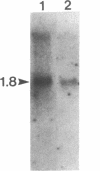
The sequence of a cDNA clone that includes the complete coding region of tryptophan decarboxylase (EC 4.1.1.28, formerly EC 4.1.1.27) from periwinkle (Catharanthus roseus) is reported. The cDNA clone (1747 base pairs) was isolated by antibody screening of a cDNA expression library produced from poly(A)+ RNA found in developing seedlings of C. roseus. The clone hybridized to a 1.8-kilobase mRNA from developing seedlings and from young leaves of mature plants. The identity of the clone was confirmed when extracts of transformed Escherichia coli expressed a protein containing tryptophan decarboxylase enzyme activity. The tryptophan decarboxylase cDNA clone encodes a protein of 500 amino acids with a calculated molecular mass of 56,142 Da. The amino acid sequence shows a high degree of similarity with the aromatic L-amino acid decarboxylase (dopa decarboxylase) and the alpha-methyldopa-hypersensitive protein of Drosophila melanogaster. The tryptophan decarboxylase sequence also showed significant similarity to feline glutamate decarboxylase and mouse ornithine decarboxylase, suggesting a possible evolutionary link between these amino acid decarboxylases.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Albert V. R., Allen J. M., Joh T. H. A single gene codes for aromatic L-amino acid decarboxylase in both neuronal and non-neuronal tissues. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jul 5;262(19):9404–9411. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aviv H., Leder P. Purification of biologically active globin messenger RNA by chromatography on oligothymidylic acid-cellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jun;69(6):1408–1412. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.6.1408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bossa F., Martini F., Barra D., Voltattorni C. B., Minelli A., Turano C. The chymotryptic phosphopyridoxyl peptide of DOPA decarboxylase from pig kidney. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1977 Sep 9;78(1):177–184. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(77)91237-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christenson J. G., Dairman W., Udenfriend S. On the identity of DOPA decarboxylase and 5-hydroxytryptophan decarboxylase (immunological titration-aromatic L-amino acid decarboxylase-serotonin-dopamine-norepinephrine). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Feb;69(2):343–347. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.2.343. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Luca V., Fernandez J. A., Campbell D., Kurz W. G. Developmental Regulation of Enzymes of Indole Alkaloid Biosynthesis in Catharanthus roseus. Plant Physiol. 1988 Feb;86(2):447–450. doi: 10.1104/pp.86.2.447. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eveleth D. D., Gietz R. D., Spencer C. A., Nargang F. E., Hodgetts R. B., Marsh J. L. Sequence and structure of the dopa decarboxylase gene of Drosophila: evidence for novel RNA splicing variants. EMBO J. 1986 Oct;5(10):2663–2672. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04549.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eveleth D. D., Marsh J. L. Evidence for evolutionary duplication of genes in the dopa decarboxylase region of Drosophila. Genetics. 1986 Oct;114(2):469–483. doi: 10.1093/genetics/114.2.469. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gubler U., Hoffman B. J. A simple and very efficient method for generating cDNA libraries. Gene. 1983 Nov;25(2-3):263–269. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90230-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones J. D., Dunsmuir P., Bedbrook J. High level expression of introduced chimaeric genes in regenerated transformed plants. EMBO J. 1985 Oct;4(10):2411–2418. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03949.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahana C., Nathans D. Nucleotide sequence of murine ornithine decarboxylase mRNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Mar;82(6):1673–1677. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.6.1673. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi Y., Kaufman D. L., Tobin A. J. Glutamic acid decarboxylase cDNA: nucleotide sequence encoding an enzymatically active fusion protein. J Neurosci. 1987 Sep;7(9):2768–2772. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.07-09-02768.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyte J., Doolittle R. F. A simple method for displaying the hydropathic character of a protein. J Mol Biol. 1982 May 5;157(1):105–132. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90515-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOVENBERG W., WEISSBACH H., UDENFRIEND S. Aromatic L-amino acid decarboxylase. J Biol Chem. 1962 Jan;237:89–93. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lütcke H. A., Chow K. C., Mickel F. S., Moss K. A., Kern H. F., Scheele G. A. Selection of AUG initiation codons differs in plants and animals. EMBO J. 1987 Jan;6(1):43–48. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04716.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maneckjee R., Baylin S. B. Use of radiolabeled monofluoromethyl-Dopa to define the subunit structure of human L-Dopa decarboxylase. Biochemistry. 1983 Dec 20;22(26):6058–6063. doi: 10.1021/bi00295a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marques I. A., Brodelius P. E. Elicitor-Induced l-Tyrosine Decarboxylase from Plant Cell Suspension Cultures : II. Partial Characterization. Plant Physiol. 1988 Sep;88(1):52–55. doi: 10.1104/pp.88.1.52. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan B. A., Johnson W. A., Hirsh J. Regulated splicing produces different forms of dopa decarboxylase in the central nervous system and hypoderm of Drosophila melanogaster. EMBO J. 1986 Dec 1;5(12):3335–3342. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04648.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson W. R., Lipman D. J. Improved tools for biological sequence comparison. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(8):2444–2448. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.8.2444. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Short J. M., Fernandez J. M., Sorge J. A., Huse W. D. Lambda ZAP: a bacteriophage lambda expression vector with in vivo excision properties. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Aug 11;16(15):7583–7600. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.15.7583. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tancini B., Dominici P., Simmaco M., Schininà M. E., Barra D., Voltattorni C. B. Limited tryptic proteolysis of pig kidney 3,4-dihydroxyphenylalanine decarboxylase. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1988 Feb 1;260(2):569–576. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(88)90483-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson M. E. Compilation of published signal sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jul 11;12(13):5145–5164. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.13.5145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]