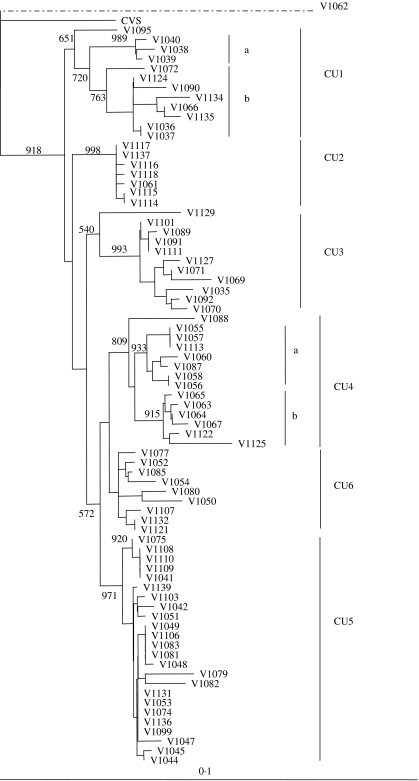
Fig. 2.
Phylogenetic tree of all Cuban isolates sequenced in this study. The tree was generated by a neighbour-joining algorithm as described using partial rabies virus N gene sequences (530 bp). The CVS strain was used as an outgroup for the terrestrial isolates although the single bat specimen (V1062) was found to be the most divergent isolate within the sample set. Bootstrap values (out of 1000 data replicates) are indicated on many of the main branches and the major clades described in the text are illustrated to the right of the tree. A genetic scale is shown at bottom; the dashed line connecting V1062 indicates that this branch is not to scale.