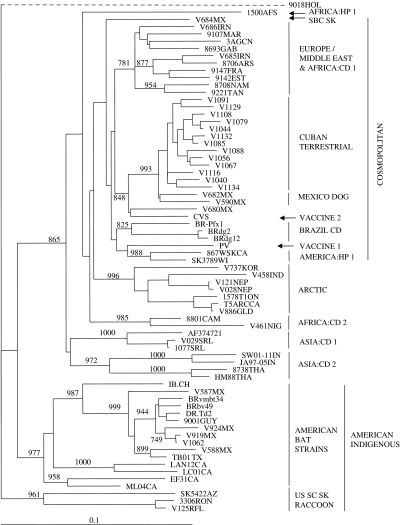
Fig. 3.
Phylogenetic tree illustrating the placement of the Cuban rabies viruses in a global context. Partial N gene sequences (630 bp) for selected Cuban isolates were aligned with corresponding sequences representative of many rabies virus strains worldwide (see list in Table 3) together with an EBLV-2 sequence as outgroup; a tree was generated using a neighbour-joining algorithm. Bootstrap values (out of 1000 replicates) are shown on all main branches and major rabies strain groupings are illustrated to the right of the tree using the following abbreviations: CD, canid type; HP, herpestid type; SBC SK, South Baja California skunk variant; US SC SK, United States south central skunk variant. Many of these groups have been described previously [14]. A genetic scale is shown at bottom; the dashed line connecting the EBLV-2 sequence (9018HOL) indicates that this branch is not to scale.