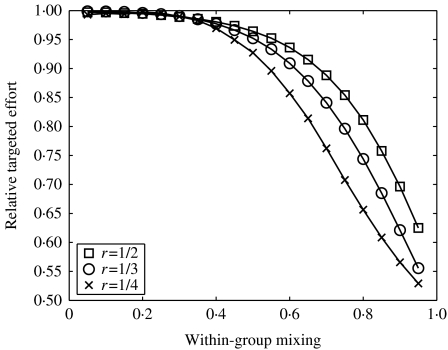
Fig. 7.
The effect of mixing pattern on the required effort to eradicate infection, using the iterative tracing model in a simplified population consisting of two types of individual. Relative targeted effort is defined to be the effort needed when tracing is optimally targeted divided by the effort required when tracing is applied uniformly. Within-group mixing is defined to be the proportion of contacts that are between individuals in the same group. In this case, effort is targeted according to the properties of the index case.