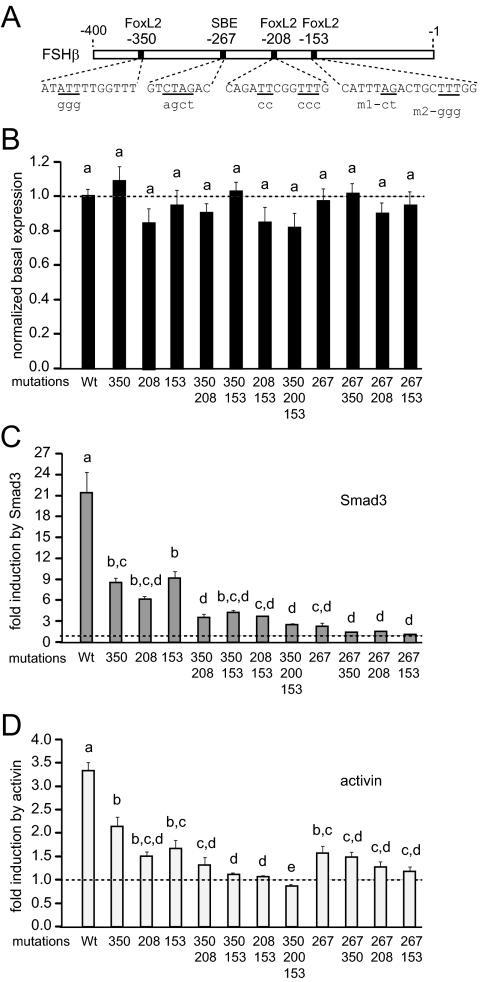
Figure 7.
The FoxL2 elements at −350, −208, and −153 are necessary for full FSHβ promoter response to caALK7 and activin. A, Location of the FoxL2 sites, identified by sequence analysis and confirmed by EMSA, on the mouse FSHβ promoter. Wild-type sequence is represented by uppercase letters, residues that were mutated are underlined, and mutations are listed in lowercase underneath. Two different mutations (m1 and m2) of the −153 site were created, but had the same effect; thus, only results with m2 are presented. B, The FoxL2 sites were mutated and the activity of mutant reporters compared with the activity of the wild-type reporter to assess the effect of mutations on basal gene expression. C and D, The effects of the mutations of the FoxL2 sites individually or in combination, and in comparison with the mutation of the −267 Smad response element, were analyzed in response to overexpression of Smad3 (C), or activin treatment (D). Bars not connected by the same letters are significantly different, P < 0.05.