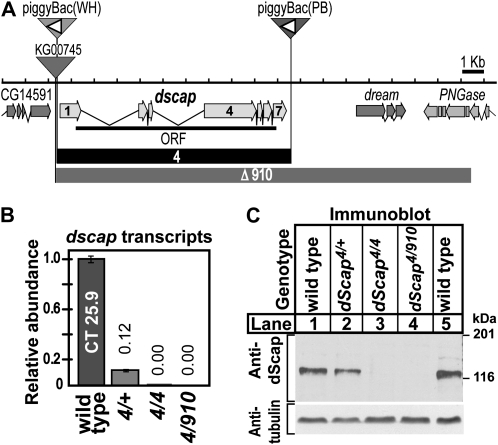
Figure 1.—
(A) Map of dScap locus. The dScap gene comprises seven exons (block arrows with light shading) encoding one protein (ORF, thick solid line). Sites of transposon insertion are indicated by inverted triangles. P-element transposon KG00745 and piggyBac(WH)f04534 are inserted prior to the start of dScap of exon 1 and after CG14591. PiggyBac(PB)c00785 is inserted 88 bp after dscap exon 7. The orientation of the FRT sites within both piggyBac elements are indicated by the open triangles. The extent of dscap4 and dscapΔ910 deletions are indicated by solid boxes and boxes with dark shading, respectively. (B) Quantitative analysis of dScap mRNA from dscap4 homozygous and dscapΔ910/dscap4 transheterozygous larvae compared to wild type (wt = 1). Numbers above bars indicate the relative abundance of transcript. Error bars represent the standard deviation. (C) Immunoblot analysis of whole larval lysates from third instar larvae of the indicated genotype (60 μg total protein/lane). Virgin dscap4/dscap4 females were crossed to either dscap4/CyO, act-GFP or dscapΔ910/CyO, act-GFP males. Embryos were seeded onto dishes containing semidefined media at 10 mg/dish. Larvae were isolated from the food by salt flotation and homozygous larvae were scored for absence of act-GFP fluorescence. The membrane was probed with monoclonal antibody IgG7A8 against dScap TM1-8 (1-min-30-sec exposure), stripped, and reprobed with anti-acetylated tubulin (2-sec exposure).