TABLE 2.
Summary of support for specific models using LBF approximated with harmonic mean (HM) and thermodynamic integration (TI) using 16 chains with different scalers
Evidence (“true” 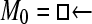 ▪) ▪) |
Counts (based on LBFTI and LBFHM) | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| nparam | 4 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 1 | ||||||||
| Model | □⇆▪ |
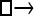 ▪ ▪ |
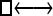 ▪ ▪ |
□⇆□ | 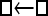 |
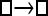 |
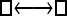 |
 |
||||||||
| Approximation | TI | HM | TI | HM | TI | HM | TI | HM | TI | HM | TI | HM | TI | HM | TI | HM |
| Against M0 | 0 | 46 | 28 | 36 | 0 | 48 | 0 | 57 | 70 | 50 | 54 | 35 | 0 | 59 | 11 | 40 |
| Against Mi | 100 | 54 | 72 | 64 | 100 | 52 | 100 | 43 | 30 | 50 | 46 | 65 | 100 | 41 | 89 | 60 |
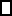
One hundred single-locus data sets were analyzed, each with a total of 20 DNA sequences simulated using a three-parameter model with two different population sizes and unidirectional migration from population 2 to population 1 (model abbreviation is 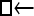 ▪). All other models 1–8 (Mi), such as the full model (□⇆▪) or the minimal model (
▪). All other models 1–8 (Mi), such as the full model (□⇆▪) or the minimal model (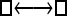 ), are compared with this “true” model (
), are compared with this “true” model (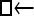 ▪), which represents the M0 hypothesis. nparam: number of parameter estimated.
▪), which represents the M0 hypothesis. nparam: number of parameter estimated.
