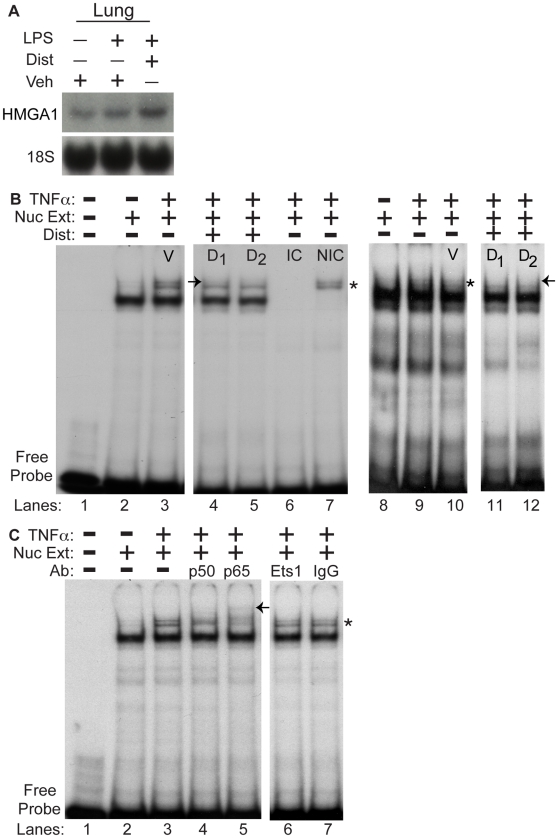
Figure 5. Distamycin A disrupts binding of an inducible protein-DNA complex containing NF-κB to an AT-rich region of the P-selectin promoter.
A. As in Fig. 3B, lung tissue was harvested from wild type mice two hours following treatment with Vehicle (Veh), LPS/Vehicle, or LPS/Dist A (Dist), then subjected to RNA extraction. The same blot from Fig. 3B was hybridized with a radiolabeled probe for HMGA1 (and an 18S probe as loading control). This experiment was repeated two separate times. B. Nuclear extracts from BAEC cells (Lanes 1–7) and primary murine lung endothelial cells (MLEC, Lanes 8–12) (“Nuc Ext”) with (Lanes 3–7, 9–12) or without (Lanes 2,8) TNF-α stimulation were subjected to electrophoretic mobility shift assays (EMSA) using a radiolabeled probe spanning the AT-rich region of the P-selectin promoter (basepairs −542 to −521). Lane 1 represents the radiolabeled probe without addition of nuclear extract. TNF-α-treated nuclear extract was additionally incubated and electrophoresed with the radiolabeled probe and vehicle (V, lanes 3 and 10 (or in the presence of TNF-α without vehicle, Lane 9)) or increasing concentrations of Dist A (D1 = 10 µM, D2 = 20 µM, Lanes 4–5, 11–12) as well as with an identical competitor (IC, Lane 6) and a non-identical competitor (NIC, Lane 7). (* represents the inducible, specific complex seen following TNF-α treatment; “→” represents disruption of the TNF-α-inducible complex following addition of Dist A (Lanes 4–5 compared with Lane 3 and Lanes 11–12 compared with Lane 9–10). All of the binding studies were repeated at least two separate times. C. Nuclear extracts from BAEC cells (“Nuc Ext”) with (Lanes 3–7) or without (Lane 2) TNF-α stimulation were subjected to electrophoretic mobility shift assays (EMSA) using a radiolabeled probe spanning the AT-rich region of the P-selectin promoter (basepairs −542 to −521). Lane 1 represents the radiolabeled probe without addition of nuclear extract. TNF-α-treated nuclear extract was additionally incubated and electrophoresed with the radiolabeled probe and antibodies to the NF-κB family members p50 and p65 (lanes 4–5), or unrelated and control antibodies (Ets-1 and IgG control respectively, lanes 6–7). (* represents the inducible, specific complex seen following TNF-α treatment; “←” represents supershifted band/disruption of the TNF-α-inducible complex following addition of p50 and p65 antibodies (Lanes 4-5 compared with Lanes 6–7). All of the binding studies were repeated at least two separate times.