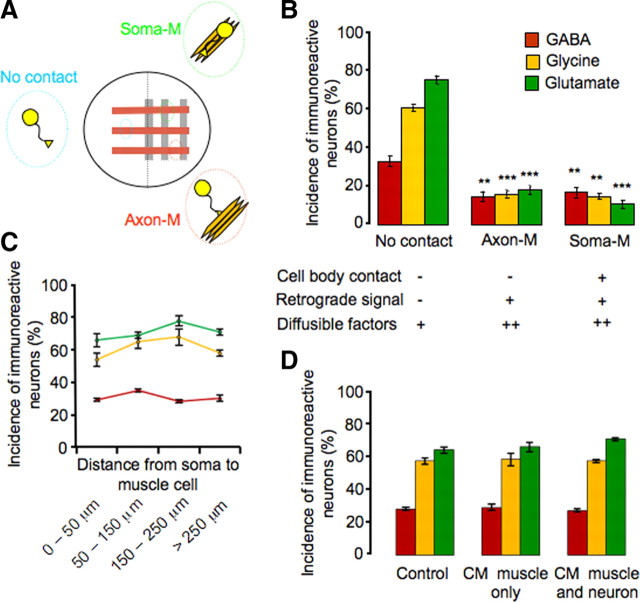
Figure 4.
Cell contacts and not diffusible factors regulate muscle-dependent suppression of noncholinergic neurotransmitter expression. A, Schematic view of the lattice neuron–muscle coculture and groups of neurons with different interactions with muscles. B, Neurons with or without cell body interaction with muscle show similar levels of reduction in incidence of noncholinergic transmitter expression, when compared with the no-contact group. There is no significant difference in noncholinergic transmitter expression between axon-M and soma-M groups (**p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001; n > 5 cultures per condition per transmitter, >100 neurons per culture). C, The incidence of expression of the three noncholinergic transmitters in the no-contact group from B (GABA in red, glycine in yellow, and glutamate in green) does not change as a function of distance from neuronal soma to muscle cells (>100 neurons scored at each distance for each transmitter). D, The incidence of expression of the three noncholinergic transmitters does not differ between the control condition and conditioned medium condition (muscle alone or muscle cocultured with neurons) (n > 5 cultures per condition per transmitter, >100 neurons per culture). Error bars indicate SEM. The Kruskal–Wallis test and Conover post hoc test were used to determine statistical significance.