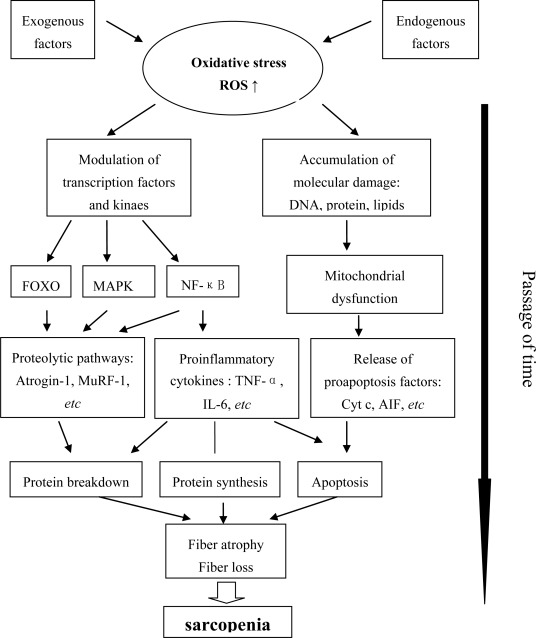
Figure 1.
A schematic summary of proposed mechanisms by which oxidative stress and chronic inflammation could contribute to sarcopenia. Some major signaling pathways are activated or inactivated during the oxidative stress and chronic inflammation seen in aged skeletal muscle. The pathways are related to an imbalance of protein synthesis and breakdown, mitochondrial dysfunction, and apoptosis, leading to fiber atrophy and fiber loss, eventually to sarcopenia.