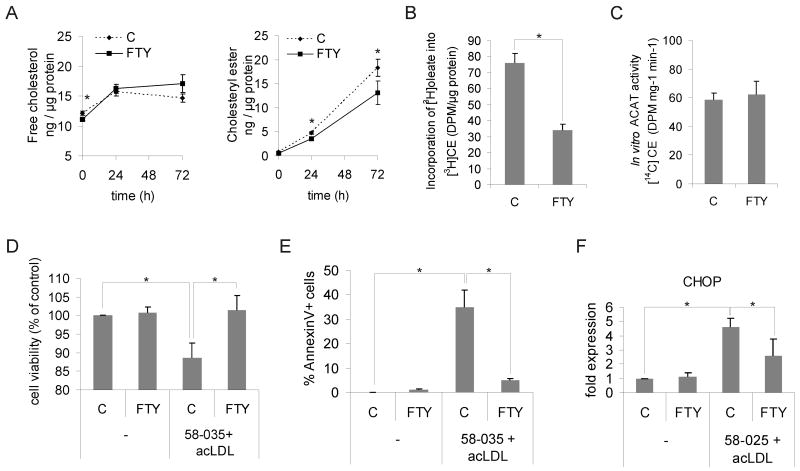
Figure 1. FTY720 alters cholesterol homeostasis and improves survival of human macrophage foam cells.
A. Macrophages were pre-treated for 24 h ± 1 μmol/L FTY720 and foam cell formation induced by addition of 50 μg/mL acLDL for 24 h or 72 h in the continued presence or absence of FTY720. Cellular free cholesterol and cholesteryl esters were determined from at least 12 independent donors per condition (C = control, FTY = FTY720). B. Cholesterol esterification was measured as [3H]oleic acid incorporation into cholesteryl esters (CE). Cells were treated ± 1 μmol/L FTY720 for 24 h, followed by a 6-h incorporation with [3H]oleic acid in the presence of 50 μg/mL acLDL. Measurements are from three independent donors. C. Determination of ACAT activity from cell lysates. Macrophages were treated for 24 h ± 1 μmol/L FTY720 prior to cell lysis and in vitro ACAT activity measured in the continued presence or absence of 1 μmol/L FTY720. Results are from 6 independent donors. D. Macrophages were treated for 24 h ± 1 μmol/L FTY720 followed by loading with 50 μg/mL acLDL in the presence of the ACAT inhibitor PKF 58-035 (10 μg/mL) for 16 h. Cell viability was then measured from three donors in triplicate. E. Macrophages were treated ± 1μmol/L FTY720 for 24 h and loaded with 50 μg/mL acLDL in the presence of PKF 58-035 for 8 h. Externalized phosphatidylserine was stained with FITC-conjugated Annexin V, and the fraction of positive cells was counted. A minimum of 180 cells from three separate fields were quantified. F. Macrophages were treated for 24 h ± 1 μmol/L FTY720, and then incubated for 48 h with 100 μg/mL acLDL and PKF 58-035. Cellular CHOP levels were quantified by Western blotting from three independent donors.