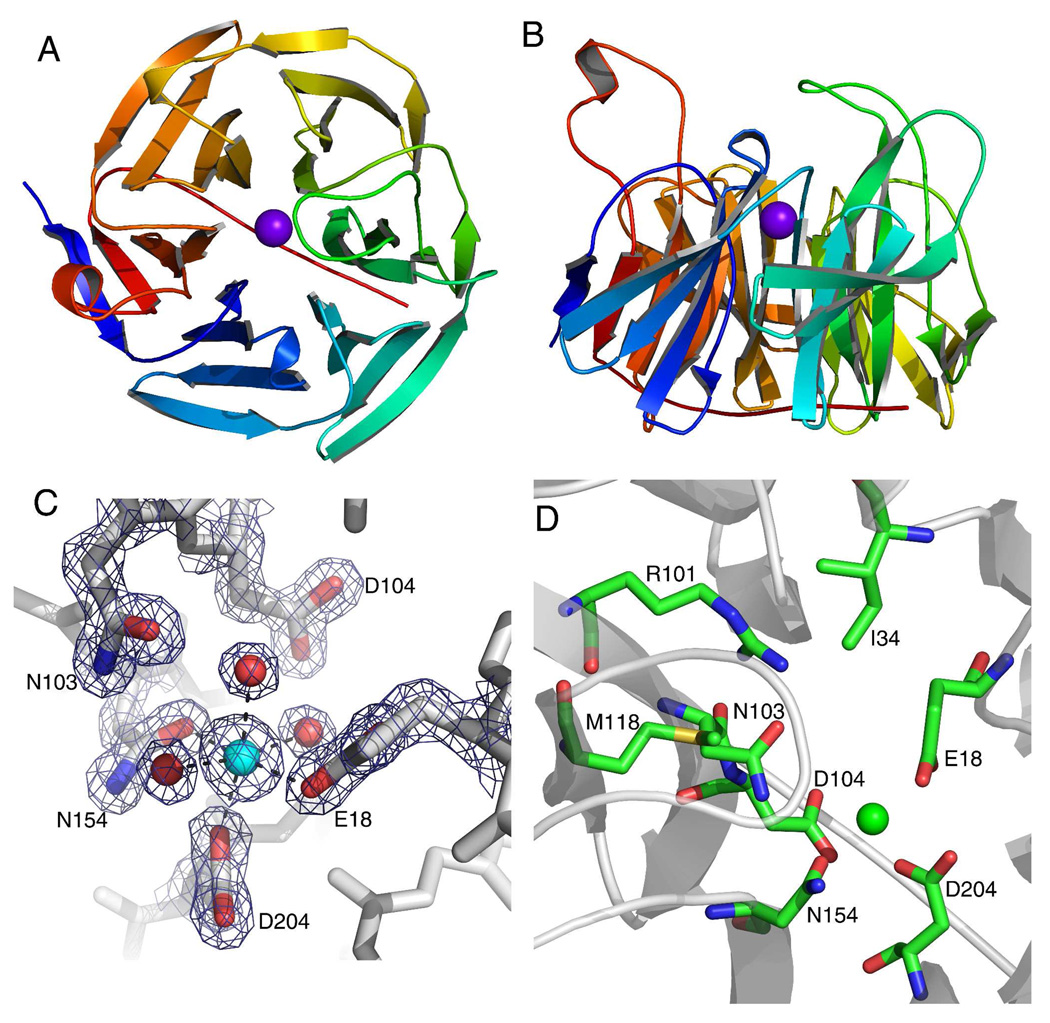
Figure 2.
The crystal structure of human SMP30 with Ca2+ bound. A, the ribbon structure of SMP30 displays the six-bladed β-propeller fold with each blade displayed in a rainbow color. The active site Ca2+ is shown in the middle of the β-propeller as a purple sphere. B, a 90° x-axis rotation of the view in panel-A displaying the loops which project up from the β-sheets and define the surface around the active site. The active site is located just above the location of the Ca2+ in this view. C, the metal binding site of human SMP30 with an electron density map (coefficients 2Fo-Fc, 2.0σ) around highlighted residues. The residues E18, D204 and N154 are bound to the Ca2+. Three water molecules complete the ligation of the hexa-coordinate Ca2+. The residues N103 and D104 are near the Ca2+, but not within bonding distance. D, The active site residues of SMP30 are shown. In addition to residues surrounding the Ca2+ (also shown in panel-C) three additional residues whose side-chains are exposed to the putative-substrate binding pocket are shown (I34, R101 and M118).