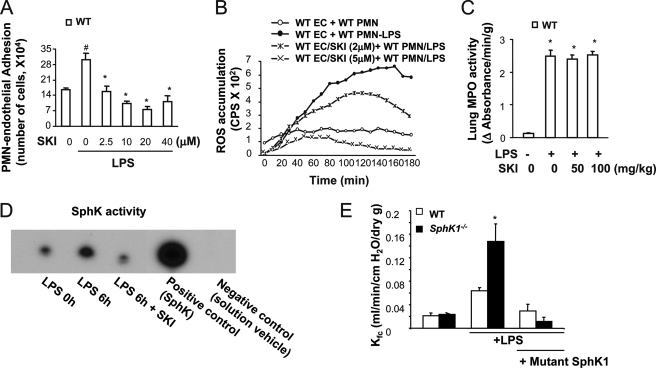
FIGURE 5.
Effects of inhibition of SphK on neutrophil adhesion to endothelial cells, neutrophil oxidant generation, and neutrophil sequestration and lung vascular permeability. A, neutrophil adhesion to WT MLVEC in the presence or absence of the SphK inhibitor SKI. # denotes increase (p < 0.05) compared with unchallenged control cells; * denotes decrease (p < 0.05) compared with non-SKI, but with LPS-treated cells. Results are means of four independent experiments; bars indicate means ± S.E. B, superoxide generation in the presence and absence of SKI. The figure shows representative curves from one of three independent experiments that produced similar results. C, lung neutrophil sequestration as measured by MPO activity in the presence and absence of SKI. * denotes increase (p < 0.05) compared with unchallenged control cells. Results are mean of four independent experiments; bars indicate mean ± S.E. D, examination of SphK activity. SphK inhibitor SKI prevented the activation of SphK induced by LPS. E, change of microvessel permeability (measured as Kf,c) in WT and SphK1−/− lungs from mice transduced with the mutant SphK1 plasmid in the presence and absence of LPS challenge (10 mg/kg, intraperitoneal). PMN, polymorphonuclear leukocytes; EC, endothelial cells.