FIGURE 1.
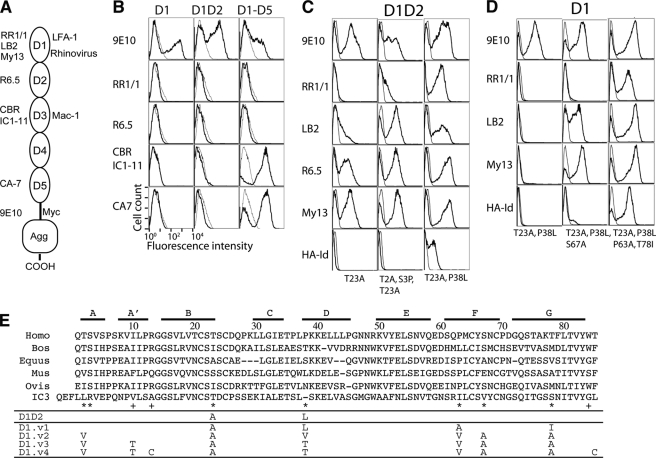
Directed evolution approach to engineer a functional single Ig superfamily domain of ICAM-1. A, ICAM-1 contains five extracellular Ig superfamily domains, recognized by different antibodies. Domains 1 and 3 of ICAM-1 serve as ligands for integrins LFA-1 (αLβ2) and Mac-1 (αMβ2) respectively. mAb RR1/1, My13, and LB2 bind to D1; R6.5 binds to D2; CBR 1C1–11 binds to D4; CA-7 binds to D5. HA-Id, high affinity I domain. Agg, agglutinin. B, ICAM-1 expression in wild-type D1, D1D2, and D1-D5 as detected by immunofluorescence flow cytometry with the indicated antibodies is shown. mAb 9E10 is against the Myc tag that is fused to ICAM-1 at the C terminus. C and D, the isolation of functional mutants of D1 and D1D2 is shown. The binding of antibodies and high affinity I domain (tetrameric HA I domain (39)) to induced yeast cells was measured by immunofluorescence flow cytometry. Throughout the figures, ligand binding to induced yeast clones is shown as a histogram drawn in a thick line and to uninduced clones as a control in a thin line. The mutations found in the clones are indicated. E, shown is evolution of engineered ICAM-1 D1 variants, aligned with ICAM-1 D1 of different species and human ICAM-3 D1. Above the sequence alignment are shown the β strands, A–G. The asterisk and plus symbols identify the positions, respectively, where mutations were found from library screening and where the mutations were designed.