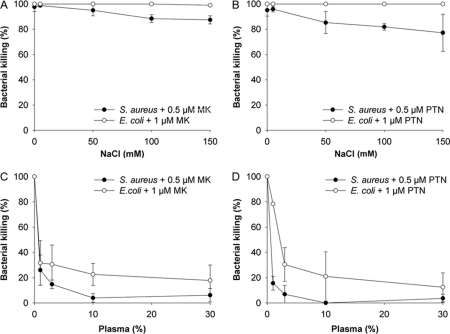
FIGURE 2.
Antibacterial activity of human MK and PTN in the presence of salt and plasma. To investigate if the presence of sodium chloride and plasma proteins interfere with the antibacterial activity of MK and PTN, respectively, the viable count assay was used. S. aureus and E. coli were grown to mid-logarithmic phase followed by incubation with MK and PTN, respectively (0.5 μm in the case of S. aureus and 1 μm in the case of E. coli) for 1 h at 37 °C. Serial dilutions were plated and the resulting cfu counted. Decrease of antibacterial activity was seen in the case of E. coli for both MK and PTN at higher concentrations of sodium chloride. Addition of plasma showed a strong inhibition of the antibacterial activity. The data shown represent mean ± S.D. from three separate experiments.