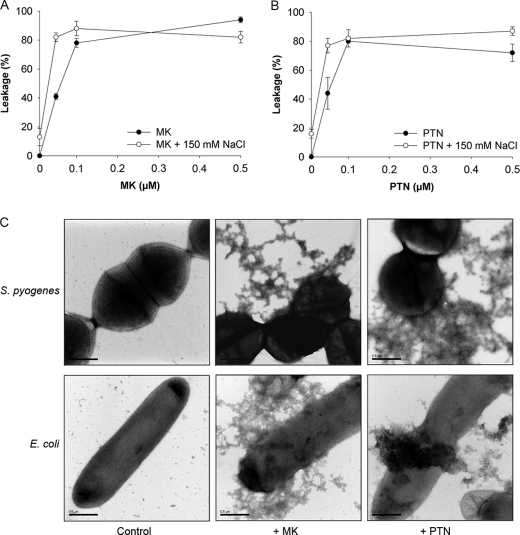
FIGURE 3.
Membrane-disrupting properties of human MK and PTN. A and B, membrane-disruptive effects of MK (A) and PTN (B) were analyzed by measuring release of carboxyfluorescein from liposomes in the absence or presence of sodium chloride (150 mm). A dose-dependent leakage, which was not affected by the presence of sodium chloride, was seen. C, ultrastructural changes of bacterial morphology after incubation with MK or PTN was investigated using electron microscopy. S. pyogenes and E. coli were incubated in buffer alone (control), and in the presence of MK or PTN (both proteins at concentrations of 0.15 μm in the case of S. pyogenes and 0.4 μm in the case of E. coli), respectively. The samples were fixed and processed for negative staining. The electron micrographs show intact bacteria after incubation in buffer (control) while incubation in the presence of MK and PTN caused bacterial disintegration with membrane blebbing and leakage of intracellular contents. Bar, 0.5 μm.