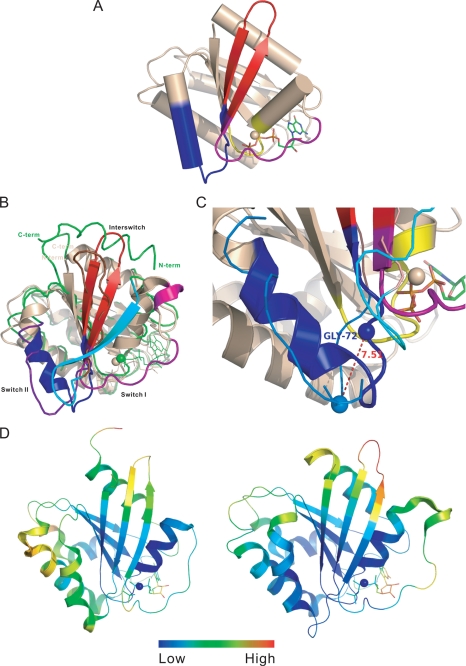
FIGURE 1.
Crystal structure of the ARL6/BBS3 small GTPase. A, cylinder representation of ARL6 structure in its GTP-bound form. The structure elements that undergo fundamental changes upon GDP/GTP exchange cycle are colored purple for switch I, blue for switch II, and red for interswitch. The P-loop is shown in yellow, and the bound GTP is shown in stick representation. B, structure comparison of GTP-bound ARL6 GTPase (PDB code 2H57) with GDP-bound full-length ARF1 GTPase (PDB code 1HUR). The structure elements undergoing fundamental conformation change in GDP/GTP exchange cycle, switch I, switch II, and interswitch, are colored purple, blue, and red for ARL6 and cyan, violet blue, and chocolate red in ARF1. All other secondary structure elements of ARL6 are presented in ribbon (wheat), although for ARF1 only Cα trace is shown (green). C, major conformational change at switch II region upon change of bound nucleotide states between ARL6 (GTP-bound) and ARF1 (GDP-bound). The color scheme is the same as in A. The Cα atoms of Gly-72 of ARL6 and corresponding Gly-70 of ARF1 are shown as spheres. D, regional conformation flexibility of GTP-bound ARF1 (left, PDB code 1O3Y) compared with that of GTP-bound ARL6 (right PDB code 2H57). The ribbons are colored according to relative B-factor of the Cα atoms, where Cα atoms with highest B-factor are colored red, and Cα atoms with lowest B-factor are colored blue.